Page 127 - JSOM Fall 2021
P. 127
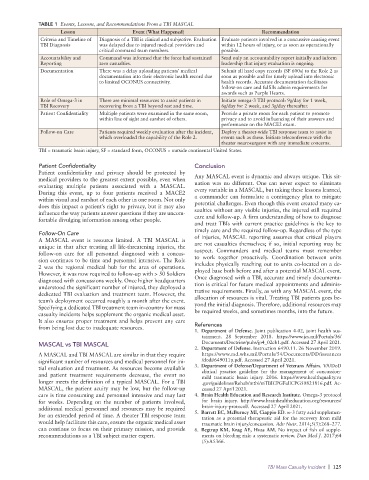
TABLE 1 Events, Lessons, and Recommendations From a TBI MASCAL
Lesson Event (What Happened) Recommendation
Criteria and Timeline of Diagnosis of a TBI is clinical and subjective. Evaluation Evaluate patients involved in a concussive causing event
TBI Diagnosis was delayed due to injured medical providers and within 12 hours of injury, or as soon as operationally
critical command team members. possible.
Accountability and Command was informed that the force had sustained Send only an accountability report initially and inform
Reporting zero casualties. leadership that injury evaluation is ongoing.
Documentation There was a delay uploading patients’ medical Submit all hard copy records (SF 600s) to the Role 2 as
documentation into their electronic health record due soon as possible and for timely upload into electronic
to limited OCONUS connectivity. health records. Accurate documentation facilitates
follow-on care and fulfills admin requirements for
awards such as Purple Hearts.
Role of Omega-3 in There are minimal resources to assist patients in Initiate omega-3 TBI protocol: 9g/day for 1 week,
TBI Recovery recovering from a TBI beyond rest and time. 6g/day for 2 week, and 3g/day thereafter.
Patient Confidentiality Multiple patients were examined in the same room, Provide a private room for each patient to promote
within line of sight and earshot of others. privacy and to avoid influencing of their answers and
performance on the MACE2 exam.
Follow-on Care Patients required weekly evaluation after the incident, Deploy a theater-wide TBI response team to assist in
which overloaded the capability of the Role 2. events such as these. Initiate teleconference with the
theater neurosurgeon with any immediate concerns.
TBI = traumatic brain injury, SF = standard form, OCONUS = outside continental United States.
Patient Confidentiality Conclusion
Patient confidentiality and privacy should be protected by
medical providers to the greatest extent possible, even when Any MASCAL event is dynamic and always unique. This sit-
evaluating multiple patients associated with a MASCAL. uation was no different. One can never expect to eliminate
During this event, up to four patients received a MACE2 every variable in a MASCAL, but taking these lessons learned,
within visual and earshot of each other in one room. Not only a commander can formulate a contingency plan to mitigate
does this impact a patient’s right to privacy, but it may also potential challenges. Even though this event created many ca-
influence the way patients answer questions if they are uncom- sualties without any visible injuries, the injured still required
fortable divulging information among other people. care and follow-up. A firm understanding of how to diagnose
and treat TBIs with current practice guidelines is the key to
timely care and the required follow-up. Regardless of the type
Follow-On Care
A MASCAL event is resource limited. A TBI MASCAL is of injuries, MASCAL reporting assumes that critical players
unique in that after treating all life-threatening injuries, the are not casualties themselves; if so, initial reporting may be
follow-on care for all personnel diagnosed with a concus- suspect. Commanders and medical teams must remember
sion continues to be time and personnel intensive. The Role to work together proactively. Coordination between units
2 was the regional medical hub for the area of operations. includes physically reaching out to units co-located on a de-
However, it was now required to follow-up with > 50 Soldiers ployed base both before and after a potential MASCAL event.
diagnosed with concussions weekly. Once higher headquarters Once diagnosed with a TBI, accurate and timely documenta-
understood the significant number of injured, they deployed a tion is critical for future medical appointments and adminis-
dedicated TBI evaluation and treatment team. However, the trative requirements. Finally, as with any MASCAL event, the
team’s deployment occurred roughly a month after the event. allocation of resources is vital. Treating TBI patients goes be-
Specifying a dedicated TBI treatment team in-country for mass yond the initial diagnosis. Therefore, additional resources may
casualty incidents helps supplement the organic medical asset. be required weeks, and sometimes months, into the future.
It also ensures proper treatment and helps prevent any care
from being lost due to inadequate resources. References
1. Department of Defense. Joint publication 4-02, joint health sus-
tainment. 28 September 2018. https://www.jcs.mil/Portals/36/
Documents/Doctrine/pubs/jp4_02ch1.pdf. Accessed 27 April 2021.
MASCAL vs TBI MASCAL
2. Department of Defense. Instruction 6490.11. 26 November 2019.
A MASCAL and TBI MASCAL are similar in that they require https://www.esd.whs.mil/Portals/54/Documents/DD/issuances
significant number of resources and medical personnel for ini- /dodi/649011p.pdf. Accessed 27 April 2021.
tial evaluation and treatment. As resources become available 3. Department of Defense/Department of Veterans Affairs. VA/DoD
and patient treatment requirements decrease, the event no clinical practice guideline for the management of concussion-
mild traumatic brain injury. 2016. https://www.healthquality.va
longer meets the definition of a typical MASCAL. For a TBI .gov/guidelines/Rehab/mtbi/mTBICPGFullCPG50821816.pdf. Ac-
MASCAL, the patient acuity may be low, but the follow-up cessed 27 April 2021.
care is time consuming and personnel intensive and may last 4. Brain Health Education and Research Institute. Omega-3 protocol
for weeks. Depending on the number of patients involved, for brain injury. http://www.brainhealtheducation.org/resources/
additional medical personnel and resources may be required brain-injury-protocol/. Accessed 27 April 2021.
for an extended period of time. A theater TBI response team 5. Barrett EC, McBurney MI, Ciappio ED. ω-3 fatty acid supplemen-
tation as a potential therapeutic aid for the recovery from mild
would help facilitate this care, ensure the organic medical asset traumatic brain injury/concussion. Adv Nutr. 2014;5(3):268–277.
can continue to focus on their primary mission, and provide 6. Begtrup KM, Krag AE, Hvas AM. No impact of fish oil supple-
recommendations as a TBI subject matter expert. ments on bleeding risk: a systematic review. Dan Med J. 2017;64
(5):A5366.
TBI Mass Casualty Incident | 125