Page 124 - JSOM Winter 2017
P. 124
segment of the eye will be affected, leading to irreversible
vision loss. The aqueous drain system can become blocked
owing to anatomic variations, changes in lens size, inflam-
mation, and trauma (Figure 20).
Figure 18 Advanced
corneal ulcer. (©2017
American Academy of
Ophthalmology, reprinted
with permission.) Figure 20 Angle-closure
glaucoma. (©2017
American Academy of
o Initiate pain control as needed. DO NOT use topical Ophthalmology, reprinted
anesthetics for pain control; they significantly impair with permission.)
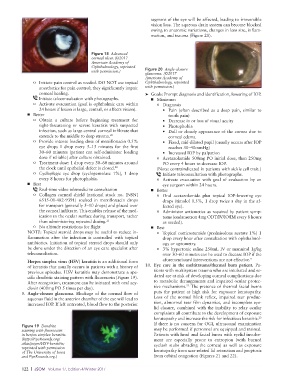
corneal healing. ➤ Goals: Prompt diagnosis and identification, lowering of IOP.
Initiate teleconsultation with photographs. ■ Minimum
o Activate evacuation (goal is ophthalmic care within o Diagnosis
24 hours if lesion is large, central, or affects vision). • Pain (often described as a deep pain, similar to
■ Better tooth pain)
o Obtain a culture before beginning treatment for • Decrease in or loss of visual acuity
sight-threatening or severe keratitis with suspected • Photophobia
infection, such as large central corneal infiltrate that • Dull or cloudy appearance of the cornea due to
extends to the middle to deep stroma. 20 corneal edema
o Provide intense loading dose of moxifloxacin 0.5% • Fixed, mid-dilated pupil (usually occurs after IOP
eye drops 1 drop every 5–15 minutes for the first reaches 30–40mmHg)
30–60 minutes (patient can self-administer loading • Increased IOP by palpation
dose if reliable) after culture obtained. o Acetazolamide 500mg PO initial dose, then 250mg
o Treatment dose: 1 drop every 30–60 minutes around PO every 4 hours to decrease IOP.
the clock until epithelial defect is closed. 20 (Note: contrain dicated in patients with sickle cell trait.)
o Cycloplegic eye drop (cyclopentolate 1%), 1 drop Initiate teleconsultation with photographs.
every 8 hours for photophobia. o Activate evacuation with goal of evaluation by an
■ Best eye surgeon within 24 hours.
Real-time video telemedicine consultation ■ Better
o Collagen corneal shield (national stock no. [NSN] o Oral acetazolamide plus topical IOP-lowering eye
6515-01-482-9391) soaked in moxifloxacin drops drops (timolol 0.5%, 1 drop twice a day in the af-
for transport (generally 5–10 drops) and placed over fected eye).
the corneal infiltrate. This enables release of the med- o Administer antiemetics as required by patient symp-
ication to the ocular surface during transport, rather toms (ondansetron 4mg ODT/IV/IO/IM every 8 hours
than administering repeated dosing. 21 as needed).
o No altitude restrictions for flight ■ Best
NOTE: Topical steroid drops may be useful to reduce in- o Topical corticosteroids (prednisolone acetate 1%) 1
flammation after the infection is controlled with topical drop every hour after consultation with ophthalmol-
antibiotics. Initiation of topical steroid drops should only ogy or optometry.
be done under the direction of an eye care specialist after o 3% hypertonic saline 250mL IV or mannitol 1g/kg
teleconsultation. over 30–60 minutes can be used to decease IOP if the
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) keratitis is an additional form aforementioned interventions are not effective. 9
of keratitis that usually occurs in patients with a history of 10. Eye care in the multitrauma/thermal burn patient. Pa-
previous episodes. HSV keratitis may demonstrate a spe- tients with multisystem trauma who are intubated and se-
cific dendritic staining pattern with fluorescein (Figure 19). dated are at risk of developing corneal complications due
After recognition, treatment can be initiated with oral acy- to metabolic derangements and impaired ocular protec-
22
clovir (400mg PO 5 times per day). tive mechanisms. The presence of thermal facial burns
9. Angle-closure glaucoma. Blockage of the normal flow of puts the patient at high risk for exposure keratopathy.
aqueous fluid in the anterior chamber of the eye will lead to Loss of the normal blink reflex, impaired tear produc-
increased IOP. If left untreated, blood flow to the posterior tion, abnormal tear film dynamics, and incomplete eye-
lid closure, combined with the inability to relay ocular
complaints all contribute to the development of exposure
keratopathy and increase the risk for infectious keratitis. 23
If there is no concern for OGI, ultrasound examination
Figure 19 Dendrite
staining with fluorescein may be performed if personnel are equipped and trained.
in herpes simplex keratitis. Patients with head and facial burns with eyelid involve-
(http://EyeRounds.org/ ment are especially prone to entropion (with burned
atlas/pages/HSV-keratitis; eyelash stubs abrading the cornea) as well as exposure
reprinted with permission keratopathy from scar-related lid retraction and proptosis
of The University of Iowa
and EyeRounds.org.) from orbital congestion (Figures 21 and 22).
122 | JSOM Volume 17, Edition 4/Winter 2017