Page 128 - JSOM Winter 2017
P. 128
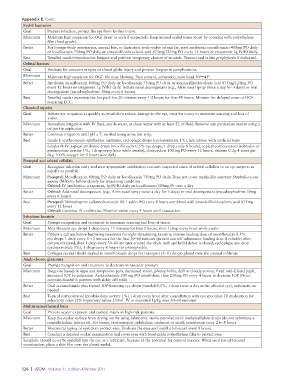
Appendix E Cont.
Eyelid laceration
Goal Prevent infection, protect the eye from further injury.
Minimum Maintain high suspicion for OGI (treat as such if suspected). Keep injured eyelid tissue moist by covering with polyethylene
film (food grade).
Better For foreign-body penetration, animal bite, or laceration with visible orbital fat, start antibiotic: moxifloxacin 400mg PO daily
or levofloxacin 750mg PO daily or amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 875mg/125mg PO every 12 hours or ertapenem 1g IV/IO daily.
Best Detailed ocular examination. Irrigate and perform temporary closure of wounds. Tetanus and rabies prophylaxis if indicated.
Orbital fracture
Goal Evaluate for concurrent open or closed globe injury and prevent long-term complications.
Minimum Maintain high suspicion for OGI. No nose blowing. Pain control, antiemetic, raise head 30°–45°.
Better Antibiotic moxifloxacin 400mg PO daily or levofloxacin 750mg PO daily or amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 875mg/125mg PO
every 12 hours or ertapenem 1g IV/IO daily. Initiate nasal decongestant (e.g., Afrin nasal spray twice a day for 3 days) or oral
decongestant (pseudoephedrine 30mg every 6 hours).
Best Detailed ocular examination. Ice pack for 20 minutes every 1-2 hours for first 48 hours. Monitor for delayed onset of OCS
requiring LCC.
Chemical injuries
Goal Initiate eye irrigation as quickly as possible to reduce damage to the eye, treat the injury to minimize scarring and loss of
vision.
Minimum Immediate irrigation with IV fluid, sterile water, or clean water with at least 2L of fluid. Remove any particulate matter using a
cotton tip applicator.
Better Continue irrigation until pH = 7, verified using urine test strip.
Best Grade I: erythromycin ophthalmic ointment, cycloplegic drops (cyclopentolate 1%), lubrication with artificial tears
Grades II–IV: topical antibiotic drops (moxifloxacin 0.5% eye drops, 1 drop every 8 hours), topical corticosteroid (tobradex or
prednisolone acetate 1%, 1 drop every hour while awake), doxycycline 100 mg PO every 12 hours, vitamin C 2g 4 times per
day, 100% oxygen for 1 hour twice daily
Preseptal and orbital cellulitis
Goal Recognize infection early and start appropriate antibiotics; evacuate suspected cases of orbital cellulitis to an eye surgeon as
rapidly as possible
Minimum Preseptal: Moxifloxacin 400mg PO daily or levofloxacin 750mg PO daily. Does not cover methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus (MRSA); follow closely for worsening condition
Orbital: IV antibiotics: ertapenem, 1g IV/IO daily or levofloxacin 500mg IV once a day
Better Orbital: Add nasal decongestant (e.g., Afrin nasal spray twice a day for 3 days) or oral decongestant (pseudoephedrine 30mg
every 6 hours)
Best Preseptal: Trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole DS 1 tablet PO every 8 hours combined with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 875mg
every 12 hours
Orbital: Continue IV antibiotics. Monitor vision every 4 hours until evacuation.
Infectious keratitis
Goal Prompt recognition and treatment to minimize scarring and loss of vision
Minimum Moxifloxacin eye drops 1 drop every 15 minutes for first 2 hours, then 1 drop every hour while awake
Better Obtain a culture before beginning treatment for sight-threatening keratitis; intense loading dose of moxifloxacin 0.5%
eye drops 1 drop every 5–15 minutes for the first 30–60 minutes (patient can self-administer loading dose if reliable) after
culture obtained; then 1 drop every 30–60 minutes around the clock until epithelial defect is closed; cycloplegic eye drop
(cyclopentolate 1%), 1 drop every 8 hours for photophobia.
Best Collagen corneal shield soaked in moxifloxacin drops for transport (5–10 drops) placed over the corneal infiltrate
Angle-closure glaucoma
Goal Prompt recognition and treatment to decrease intraocular pressure
Minimum Diagnose based on signs and symptoms: pain, decreased vision, photophobia, dull or cloudy cornea, fixed mid-dilated pupil,
increased IOP by palpation. Acetazolamide 500 mg PO initial dose, then 250mg PO every 4 hours to decrease IOP (Note:
contrain dicated in patients with sickle cell trait).
Better Oral acetazolamide plus topical IOP-lowering eye drops (timolol 0.5%, 1 drop twice a day in the affected eye), antiemetic as
needed
Best Topical corticosteroid (prednisolone acetate 1%) 1 drop every hour after consultation with eye specialist. IV medication for
refractory cases (3% hypertonic saline 250mL IV or mannitol 1g/kg over 30–60 minutes)
Multitrauma/thermal burn
Goal Prevent ocular exposure and corneal injury in high-risk patients.
Minimum Keep the ocular surface from drying out by using lubricants: sterile petrolatum or methylcellulose drops (do not substitute a
nonophthalmic lubricant). For burns, erythromycin ophthalmic ointment or sterile petrolatum every 2 to 4 hours
Better Horizontal taping of eyelids to protect eyes. Evaluate the eyes and instill a lubricant every 8 hours.
Best Conduct a detailed ocular examination and cover eyes with food-grade polyethylene film to protect eyes.
Surgilube should never be instilled into the eye as a lubricant, because of the potential for corneal toxicity. When used for ultrasound
examination, place a thin film over the closed eyelid.
126 | JSOM Volume 17, Edition 4/Winter 2017