Page 121 - JSOM Winter 2017
P. 121
o No altitude restrictions are required for evacuation.
5. Orbital fracture. Fracture of the orbital bones occurs when
an object that is larger than the width of the orbit (e.g., fist
or softball) strikes the orbit. The acute expansion of or-
bital contents and mechanical buckling forces can result in
fractures of the medial wall or orbital floor. This can cause
Figure 9 Eyelid margin
laceration. (Photograph by herniation of orbital contents into the surrounding sinuses
LTC Marcus Colyer.) and entrapment of the extraocular muscles in the fracture
site. Physical examination findings consistent with orbital
fracture include a palpable and painful step-off along the
orbital rim, enophthalmos (globe is further back in the or-
bit compared with the other eye), restricted eye movement,
and numbness below the eye (caused by damage to the in-
fraorbital nerve). Trismus and malocclusion may indicate
16
Figure 10 Complex a larger zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture. Orbital
lid laceration with fractures are not ophthalmic emergencies but may require
medial canthus avulsion. surgical treatment to prevent the complication of double
(Photograph by vision from ocular misalignment.
COL Mark Reynolds.)
➤ Goals: Evaluate for concurrent open or closed globe injury
and prevent long-term complications.
■ Minimum
o Maintain a high suspicion for associated OGI; treat
as a suspected open globe until eye surgical evalua-
tion is available.
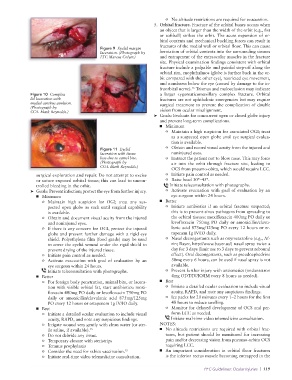
Figure 11 Eyelid o Obtain and record visual acuity from the injured and
laceration with tissue noninjured eyes.
loss due to camel bite. o Instruct the patient not to blow nose. This may force
(Photograph by air into the orbit through fracture site, leading to
COL Mark Reynolds.)
OCS from pneumo-obita, which would require LCC.
surgical exploration and repair. Do not attempt to excise o Initiate pain control as needed.
or suture exposed orbital tissue; this can lead to uncon- o Raise head 30°–45°.
trolled bleeding in the orbit. Initiate teleconsultation with photographs.
➤ Goals: Prevent infection; protect the eye from further injury. o Activate evacuation with goal of evaluation by an
■ Minimum eye surgeon within 24 hours.
o Maintain high suspicion for OGI; treat any sus- ■ Better
pected open globe as such until surgical capability o Initiate antibiotics if an orbital fracture suspected;
is available. this is to prevent sinus pathogens from spreading to
o Obtain and document visual acuity from the injured the orbital tissues: moxifloxacin 400mg PO daily or
and noninjured eyes. levofloxacin 750mg PO daily or amoxicillin/clavu-
o If there is any concern for OGI, protect the injured lanic acid 875mg/125mg PO every 12 hours or er-
globe and prevent further damage with a rigid eye tapenem 1g IV/IO daily.
shield. Polyethylene film (food grade) may be used o Nasal decongestants such as oxymetazoline (e.g., Af-
to cover the eyelid wound under the rigid shield to rin; Bayer, http://www.bayer.us/) nasal spray twice a
prevent drying of the injured tissue. day for 3 days (limit use to 3 days to prevent rebound
o Initiate pain control as needed. effect). Oral decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine
o Activate evacuation with goal of evaluation by an 30mg every 6 hours, can be used if nasal spray is not
eye surgeon within 24 hours. available.
Initiate teleconsultation with photographs. o Prevent further injury with antiemetics (ondansetron
■ Better 4mg ODT/IV/IO/IM every 8 hours as needed).
o For foreign body penetration, animal bite, or lacera- ■ Best
tion with visible orbital fat, start antibiotics: moxi- o Initiate a detailed ocular evaluation to include visual
floxacin 400mg PO daily or levofloxacin 750mg PO acuity, RAPD, and note any suspicious findings.
daily or amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 875mg/125mg o Ice packs for 20 minutes every 1–2 hours for the first
PO every 12 hours or ertapenem 1g IV/IO daily. 48 hours to reduce swelling.
■ Best o Monitor for delayed development of OCS and per-
o Initiate a detailed ocular evaluation to include visual form LCC as needed.
acuity, RAPD, and note any suspicious findings. Initiate real-time video telemedicine consultation.
o Irrigate wound very gently with clean water (or ster- NOTES:
ile saline, if available). 15 ■ No altitude restrictions are required with orbital frac-
o Do not debride any tissue. tures, but patient should be monitored for increasing
o Temporary closure with steristrips pain and/or decreasing vision from pneumo-orbita OCS
o Tetanus prophylaxis requiring LCC.
o Consider the need for rabies vaccination. 15 ■ An important consideration in orbital floor fractures
o Initiate real-time video telemedicine consultation. is the inferior rectus muscle becoming entrapped in the
PFC Guidelines: Ocular Injuries | 119