Page 125 - JSOM Fall 2025
P. 125
TABLE 1 Detailed Demographic Characteristics of the Included Studies
No. of
First author, year Setting AAJT subjects Significant findings regarding the AAJT
Balian, 2020 18 prehospital TCA patients, HEMS setting in 18 No evidence supports the clinical effectiveness of
Sydney, Australia. Clinical case series. the AAJT.
Bränsström, 2019 Animal: Comparative animal model study on 12 Transition from AAJT to REBOA was feasible with
the transition from AAJT to REBOA hemodynamic support.
Bränsström, 2022 Animal: Comparative animal model study 6 Treatment with the AAJT required one seventh of the
with REBOA. amount of crystalloids compared to REBOA. AAJT
subjects required vasopressor support upon deflation.
Do, 2019 Animal: Comparative animal model study 6 The AAJT extended survival time, decreased blood loss,
with open pelvic packing and preperitoneal achieved higher tamponade pressure, and improved
balloon tamponade. survival. Fifty percent of the subjects sustained organ
injuries, and 66% died from reperfusion injuries within
10 minutes of the release of the AAJT.
Schechtman, 2020 Animal: Comparative animal model study 10 Use of either device caused a progressive lactic acidosis,
with REBOA. reversible only by deflation of the device and whole
blood resuscitation.
Schechtman, 2020 Animal: Comparative animal model study 15 Differences in results stemmed from the choice of
with REBOA and different resuscitative fluids. resuscitative fluids instead of the AAJT or REBOA.
Smith, 2023 Healthy applications by British CMT 21 The AAJT was easy to use and regarded as having a role
operators. Volunteer study on the utility of the in saving lives by British combat medic technicians.
AAJT.
Stigall, 2020 Animal: Comparative animal model study on 18 An AAJT that is worn and inflated has the potential to
the transition from the AAJT to REBOA. cause improper REBOA cannulation if the transition is
made simultaneously.
Zhang, 2024 Animal: Comparative animal model study 6 The device used with intermittent hemostasis had the
with other junctional tourniquets. most favorable hemodynamic effects.
AAJT = abdominal aortic and junctional tourniquet; CMT = combat medic technician; HEMS = Helicopter Emergency Medical Services;
REBOA = resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta; TCA = traumatic cardiac arrest.
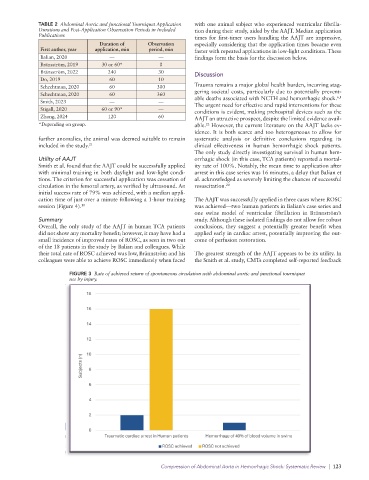
FIGURE 2 Mortality of abdominal aortic and junctional tourniquet subjects by injury.
122 | JSOM Volume 25, Edition 3 / Fall 2025