Page 126 - JSOM Fall 2025
P. 126
TABLE 2 Abdominal Aortic and Junctional Tourniquet Application with one animal subject who experienced ventricular fibrilla-
Durations and Post-Application Observation Periods in Included tion during their study, aided by the AAJT. Median application
Publications times for first-timer users handling the AAJT are impressive,
Duration of Observation especially considering that the application times became even
First author, year application, min period, min faster with repeated applications in low-light conditions. These
Balian, 2020 — — findings form the basis for the discussion below.
Bränsström, 2019 30 or 60* 0
Bränsström, 2022 240 30 Discussion
Do, 2019 60 10
Schechtman, 2020 60 300 Trauma remains a major global health burden, incurring stag-
Schechtman, 2020 60 360 gering societal costs, particularly due to potentially prevent-
able deaths associated with NCTH and hemorrhagic shock.
6,8
Smith, 2023 — — The urgent need for effective and rapid interventions for these
Stigall, 2020 60 or 90* — conditions is evident, making prehospital devices such as the
Zhang, 2024 120 60 AAJT an attractive prospect, despite the limited evidence avail-
*Depending on group. able. However, the current literature on the AAJT lacks ev-
22
idence. It is both scarce and too heterogeneous to allow for
further anomalies, the animal was deemed suitable to remain systematic analysis or definitive conclusions regarding its
included in the study. 21 clinical effectiveness in human hemorrhagic shock patients.
The only study directly investigating survival in human hem-
Utility of AAJT orrhagic shock (in this case, TCA patients) reported a mortal-
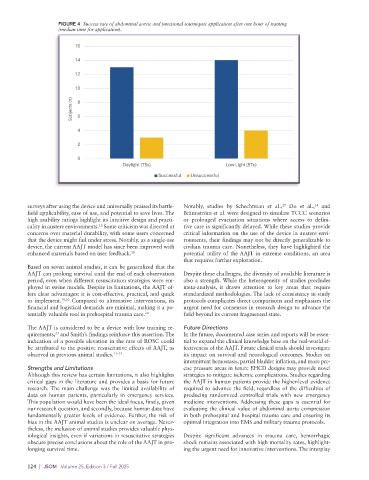
Smith et al. found that the AAJT could be successfully applied ity rate of 100%. Notably, the mean time to application after
with minimal training in both daylight and low-light condi- arrest in this case series was 16 minutes, a delay that Balian et
tions. The criterion for successful application was cessation of al. acknowledged as severely limiting the chances of successful
circulation in the femoral artery, as verified by ultrasound. An resuscitation. 20
initial success rate of 79% was achieved, with a median appli-
cation time of just over a minute following a 1-hour training The AAJT was successfully applied in three cases where ROSC
session (Figure 4). 10 was achieved—two human patients in Balian’s case series and
one swine model of ventricular fibrillation in Brännström’s
Summary study. Although these isolated findings do not allow for robust
Overall, the only study of the AAJT in human TCA patients conclusions, they suggest a potentially greater benefit when
did not show any mortality benefit; however, it may have had a applied early in cardiac arrest, potentially improving the out-
small incidence of improved rates of ROSC, as seen in two out come of perfusion restoration.
of the 18 patients in the study by Balian and colleagues. While
their total rate of ROSC achieved was low, Brännström and his The greatest strength of the AAJT appears to be its utility. In
colleagues were able to achieve ROSC immediately when faced the Smith et al. study, CMTs completed self-reported feedback
FIGURE 3 Rate of achieved return of spontaneous circulation with abdominal aortic and junctional tourniquet
use by injury.
Compression of Abdominal Aorta in Hemorrhagic Shock: Systematic Review | 123