Page 57 - JSOM Fall 2023
P. 57
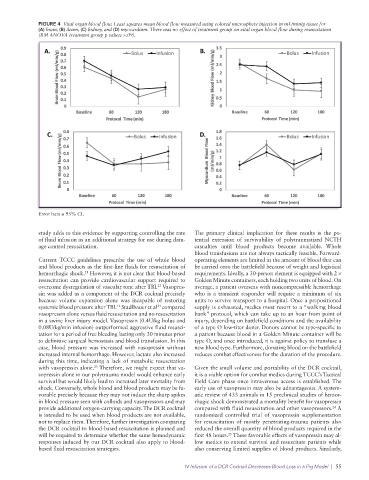
FIGURE 4 Vital organ blood flow. Least squares mean blood flow measured using colored microsphere injection in mL/min/g tissue for
(A) brain, (B) ileum, (C) kidney, and (D) myocardium. There was no effect of treatment group on vital organ blood flow during resuscitation
(RM ANOVA treatment group p values >.09).
Error bars = 95% CI.
study adds to this evidence by supporting controlling the rate The primary clinical implication for these results is the po-
of fluid infusion as an additional strategy for use during dam- tential extension of survivability of polytraumatized NCTH
age control resuscitation. casualties until blood products become available. Whole
blood transfusions are not always tactically feasible. Forward-
Current TCCC guidelines prescribe the use of whole blood operating elements are limited in the amount of blood that can
and blood products as the first-line fluids for resuscitation of be carried onto the battlefield because of weight and logistical
hemorrhagic shock. However, it is not clear that blood-based requirements. Ideally, a 30-person element is equipped with 2 ×
21
resuscitation can provide cardiovascular support required to Golden Minute containers, each holding two units of blood. On
overcome dysregulation of vascular tone after TBI. Vasopres- average, a patient overseas with noncompressible hemorrhage
22
sin was added as a component of the DCR cocktail precisely who is a transient responder will require a minimum of six
because volume expansion alone was incapable of restoring units to survive transport to a hospital. Once a prepositioned
systemic blood pressure after TBI. Stadlbauer et al compared supply is exhausted, medics must resort to a “walking blood
12
23
vasopressin alone versus fluid resuscitation and no resuscitation bank” protocol, which can take up to an hour from point of
in a swine liver injury model. Vasopressin (0.4U/kg bolus and injury, depending on battlefield conditions and the availability
0.08U/kg/min infusion) outperformed aggressive fluid resusci- of a type O low-titer doner. Donors cannot be type-specific to
tation for a period of free bleeding lasting only 30 minutes prior a patient because blood in a Golden Minute container will be
to definitive surgical hemostasis and blood transfusion. In this type O, and once introduced, it is against policy to transfuse a
case, blood pressure was increased with vasopressin without new blood type. Furthermore, donating blood on the battlefield
increased internal hemorrhage. However, lactate also increased reduces combat effectiveness for the duration of the procedure.
during this time, indicating a lack of metabolic resuscitation
with vasopressin alone. Therefore, we might expect that va- Given the small volume and portability of the DCR cocktail,
23
sopressin alone in our polytrauma model would enhance early it is a viable option for combat medics during TCCC’s Tactical
survival but would likely lead to increased later mortality from Field Care phase once intravenous access is established. The
shock. Conversely, whole blood and blood products may be fa- early use of vasopressin may also be advantageous. A system-
vorable precisely because they may not induce the sharp spikes atic review of 433 animals in 15 preclinical studies of hemor-
in blood pressure seen with colloids and vasopressors and may rhagic shock demonstrated a mortality benefit for vasopressin
provide additional oxygen-carrying capacity. The DCR cocktail compared with fluid resuscitation and other vasopressors. A
24
is intended to be used when blood products are not available, randomized controlled trial of vasopressin supplementation
not to replace them. Therefore, further investigation comparing for resuscitation of mostly penetrating-trauma patients also
the DCR cocktail to blood-based resuscitation is planned and reduced the overall quantity of blood products required in the
will be required to determine whether the same hemodynamic first 48 hours. These favorable effects of vasopressin may al-
25
responses induced by our DCR cocktail also apply to blood- low medics to extend survival and resuscitate patients while
based fluid resuscitation strategies. also conserving limited supplies of blood products. Similarly,
IV Infusion of a DCR Cocktail Decreases Blood Loss in a Pig Model | 55