Page 55 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Spring 2015
P. 55
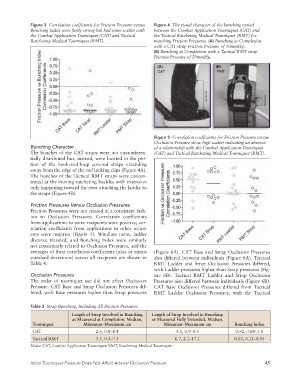
Figure 3 Correlation coefficients for Friction Pressure versus Figure 4 The visual character of the bunching varied
Bunching Index were fairly strong but had some scatter with between the Combat Application Tourniquet (CAT) and
the Combat Application Tourniquet (CAT) and Tactical the Tactical Ratcheting Medical Tourniquet (RMT) for
Ratcheting Medical Tourniquet (RMT). matching Friction Pressures. (A) Bunching at Completion
with a CAT strap Friction Pressure of 50mmHg.
(B) Bunching at Completion with a Tactical RMT strap
Friction Pressure of 50mmHg.
(A) (B)
Figure 5 Correlation coefficients for Friction Pressure versus
Occlusion Pressure show high scatter indicating an absence
Bunching Character of a relationship with the Combat Application Tourniquet
The bunches of the CAT straps were not circumferen (CAT) and Tactical Ratcheting Medical Tourniquet (RMT).
tially distributed but, instead, were located in the por
tion of the hookandloop covered straps extending
away from the edge of the rod locking clips (Figure 4A).
The bunches of the Tactical RMT straps were concen
trated at the moving ratcheting buckles with extension
only happening toward the rivet attaching the ladder to
the straps (Figure 4B).
Friction Pressures Versus Occlusion Pressures
Friction Pressures were not related in a consistent fash
ion to Occlusion Pressures: Correlation coefficients
from applications to some recipients were positive; cor
relation coefficients from applications to other recipi
ents were negative (Figure 5). Windlass turns, ladder
distance traveled, and Bunching Index were similarly
not consistently related to Occlusion Pressures, and the
averages of their correlation coefficients (plus or minus (Figure 6A). CAT Base and Strap Occlusion Pressures
standard deviations) across all recipients are shown in also differed between individuals (Figure 6A). Tactical
Table 4. RMT Ladder and Strap Occlusion Pressures differed,
with Ladder pressures higher than Strap pressures (Fig
Occlusion Pressures ure 6B). Tactical RMT Ladder and Strap Occlusion
The order of tourniquet use did not affect Occlusion Pressures also differed between individuals (Figure 6B).
Pressure. CAT Base and Strap Occlusion Pressures dif CAT Base Occlusion Pressures differed from Tactical
fered, with Base pressures higher than Strap pressures RMT Ladder Occlusion Pressures, with the Tactical
Table 3 Strap Bunching, Including All Friction Pressures
Length of Strap Involved in Bunching Length of Strap Involved in Bunching
as Measured at Completion, Median, as Measured Fully Extended, Median,
Tourniquet Minimum–Maximum cm Minimum–Maximum cm Bunching Index
CAT 2.6, 0.8–8.4 3.0, 0.9–9.5 0.92, 0.64–1.0
Tactical RMT 3.5, 0.3–7.5 6.7, 2.1–17.1 0.53, 0.11–0.95
Notes: CAT, Combat Application Tourniquet; RMT, Ratcheting Medical Tourniquet.
Initial Tourniquet Pressure Does Not Affect Arterial Occlusion Pressure 45