Page 51 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Spring 2015
P. 51
rings. The minor differences in the Tactical RMT versions Friction Pressure was recorded when the applier had
are shown in Table 1. The mechanical advantage system taken his or her hands off the tourniquet prior to engag
of the Tactical RMTs was the toothed ladder and a ratch ing the mechanical advantage tightening system. The
eting buckle. Each ladder was 1.9cm wide and had 2.5 targets for Friction Pressure were based on previously ob
teeth/cm. The ratcheting buckle of each Tactical RMT served pressures achieved by CAT and RMT appliers. 5,8
was 3.0cm wide by 4.5cm long with a 0.762cmlong
slot to allow the cam action of the advancing pawl when The target Friction Pressures for the CATs were Strap
ratcheting. The ladder was riveted to the 3.8cm fabric pressures from 50 to 200mmHg with 25mmHg incre
strap near the friction buckle. The ratcheting buckle was ments. The CATs were secured at Friction Pressure only
riveted to the 3.8cm fabric strap at the far end of the lad via the hookandloop on the strap. The CAT 3.8cmwide
der from the friction buckle. Advancing the ratcheting strap was not double threaded through the friction buckle
buckle along the ladder, therefore, shortened the distance at any time. This allowed appliers to achieve prewindlass
between the rivets, thus resulting in increasing tourni Friction Pressures all the way up to 200mmHg. The lowest
quetapplied pressure on the surface of the limb. target Friction Pressure for the CATs was set at 50mmHg
to minimize the CAT tourniquet wear that accompanies a
Pressure Measurements lack of adequate tightness before engaging the windlass. 7
Skin surfaceapplied pressures under both tourniquets
were measured using two size #1 neonatal blood pres Initially, the target Friction Pressures for the Tactical RMTs
sure cuffs (2.2cm × 6.5cm bladder, single tube). Each cuff were Strap pressures from 25 to 200mmHg with 25mmHg
was inflated 10–15mmHg above atmospheric pressure, increments. Inability of appliers to pull the strap tight
and the resulting pressure was used as the baseline. The enough to reach Friction Pressures >150mmHg with
airfilled cuffs were taped to the tourniquets. On the the Tactical RMTs on the first three recipients resulted
CAT, one cuff was taped under the strap beneath the in changing the Tactical RMT target Friction Pressures
base plate (Base); the other was taped under the strap range to 25–150mmHg.
alone at the same distance from the first cuff as was
the case with the Tactical RMT (Strap). On the Tacti Occlusion was defined as loss of the dorsalis pedis arte
cal RMT, one cuff was taped under the strap beneath rial Doppler pulse signal (Ultrasonic Doppler Flow De
the ladder at the ladder attachment point to the strap tector Model 811 with 9.5 MHz adult flat probe; Parks
(Ladder); the other was taped under the strap alone just Medical Electronics, www.parksmed.com). With the
beyond the ratcheting buckle attachment point to the CATs, tightening occurred throughout windlass turning,
strap (Strap). The inflated cuffs were connected to a and Occlusion Pressure was recorded as the pressure
gas pressure sensor system (Vernier Gas Pressure Sen present at the applierheld windlass position that had no
sor, Vernier LabPro interface, and Logger Pro Software; audible pulse signal. With the Tactical RMTs, tightening
Vernier Software and Technology, www.vernier.com). occurred tooth by tooth as the pawl was advanced, and
The pressures were continuously displayed graphically Occlusion Pressure was recorded as the pressure present
with numeric values displayed every second. Each tour with no audible pulse signal with the ratcheting buckle
niquet application’s Ladder/Base and Strap data were returned to its rest location.
saved as complete combined graphic and numeric data
with markers placed on the graph at each time point for Completion was defined as when the applier’s hands
pressure comparisons at the following events: friction were off the secured tourniquet. For the CATs, Comple
buckle secured (Friction), occlusion (Occlusion), and tion Pressure was recorded when the windlass was in
completion (Completion). the rod locking clip at the closest opportunity tighter
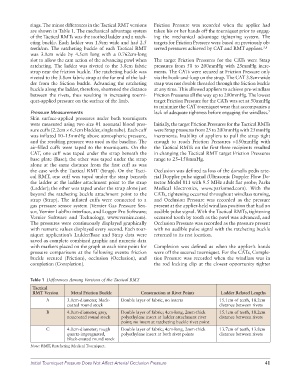
Table 1 Differences Among Versions of the Tactical RMT
Tactical
RMT Version Metal Friction Buckle Construction at Rivet Points Ladder Related Lengths
A 3.0cmdiameter, black Double layer of fabric, no inserts 15.1cm of teeth, 18.2cm
coated round stock distance between rivets
B 4.0cmdiameter, grey, Double layer of fabric; 4cmlong, 2mmthick 15.1cm of teeth, 18.2cm
noncoated round stock polyethylene insert at ladder attachment rivet distance between rivets
point; no insert at ratcheting buckle rivet point
C 4.0cmdiameter; rough Double layer of fabric; 4cmlong, 2mmthick 13.7cm of teeth, 13.8cm
quartzimpregnated, polyethylene insert at both rivet points distance between rivets
blackcoated round stock
Note: RMT, Ratcheting Medical Tourniquet.
Initial Tourniquet Pressure Does Not Affect Arterial Occlusion Pressure 41