Page 13 - JSOM Fall 2024
P. 13
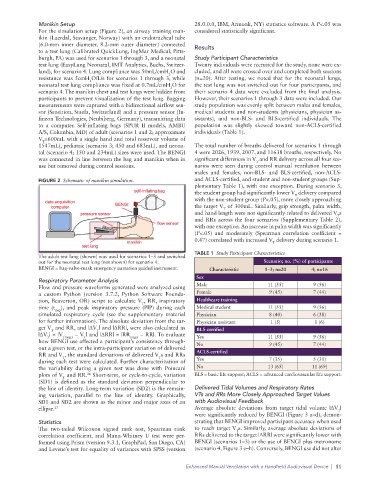
Manikin Setup 28.0.0.0, IBM, Armonk, NY) statistics software. A P<.05 was
For the simulation setup (Figure 2), an airway training man- considered statistically significant.
ikin (Laerdal, Stavanger, Norway) with an endotracheal tube
(6.0-mm inner diameter, 8.2-mm outer diameter) connected Results
to a test lung (Calibrated QuickLung, IngMar Medical, Pitts-
burgh, PA) was used for scenarios 1 through 3, and a neonatal Study Participant Characteristics
test lung (EasyLung Neonatal, IMT Analytics, Buchs, Switzer- Twenty individuals were recruited for the study, none were ex-
land), for scenario 4. Lung compliance was 50mL/cmH O and cluded, and all were crossed over and completed both sessions
2
resistance was 5cmH O/L/s for scenarios 1 through 3, while (n=20). After testing, we noted that for the neonatal lungs,
2
neonatal test lung compliance was fixed at 0.7mL/cmH O for the test lung was not switched out for four participants, and
2
scenario 4. The manikin chest and test lungs were hidden from their scenario 4 data were excluded from the final analysis.
participants to prevent visualization of the test lung. Bagging However, their scenarios 1 through 3 data were included. Our
measurements were captured with a bidirectional airflow sen- study population was evenly split between males and females,
sor (Sensirion, Staefa, Switzerland) and a pressure sensor (In- medical students and non-students (physicians, physician as-
fineon Technologies, Neubiberg, Germany), transmitting data sistants), and non-BLS- and BLS-certified individuals. The
to a computer. Self-inflating bags (SPUR II models, AMBU population was slightly skewed toward non-ACLS-certified
A/S, Columbia, MD) of adult (scenarios 1 and 2; approximate individuals (Table 1).
V =600mL with a single hand and total reservoir volume of
T
1547mL), pediatric (scenario 3; 450 and 683mL), and neona- The total number of breaths delivered for scenarios 1 through
tal (scenario 4; 150 and 234mL) sizes were used. The BENGI 4 were 2026, 1939, 2007, and 11638 breaths, respectively. No
was connected in line between the bag and manikin when in significant differences in V and RR delivery across all four sce-
T
use but removed during control sessions. narios were seen during control manual ventilation between
males and females, non-BLS- and BLS-certified, non-ACLS-
FIGURE 2 Schematic of manikin simulation. and ACLS-certified, and student and non-student groups (Sup-
plementary Table 1), with one exception. During scenario 3,
the student group had significantly lower V delivery compared
T
with the non-student group (P<.05), more closely approaching
the target V of 300mL. Similarly, grip strength, palm width,
T
and hand length were not significantly related to delivered V s
T
and RRs across the four scenarios (Supplementary Table 2),
with one exception. An increase in palm width was significantly
(P<.05) and moderately (Spearman correlation coefficient =
0.47) correlated with increased V delivery during scenario 1.
T
TABLE 1 Study Participant Characteristics
The adult test lung (shown) was used for scenarios 1–3 and switched
out for the neonatal test lung (not shown) for scenario 4. Scenario; no. (%) of participants
BENGI = bag-valve-mask emergency narration guided instrument. Characteristic 1–3; n=20 4; n=16
Sex
Respiratory Parameter Analysis
Flow and pressure waveforms generated were analyzed using Male 11 (55) 9 (56)
a custom Python (version 3.7.2, Python Software Founda- Female 9 (45) 7 (44)
tion, Beaverton, OR) script to calculate V , RR, inspiratory Healthcare training
T
time (t insp ), and peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) during each Medical student 11 (55) 9 (56)
simulated respiratory cycle (see the supplementary material Physician 8 (40) 6 (38)
for further information). The absolute deviation from the tar- Physician assistant 1 (5) 1 (6)
get V and RR, and |ΔV | and |ΔRR|, were also calculated as BLS-certified
T
T
|ΔV | = |V Ttarget − V | and |ΔRR| = |RR target − RR|. To evaluate Yes 11 (55) 9 (56)
T
T
how BENGI use affected a participant’s consistency through-
out a given test, or the intra-participant variation of delivered No 9 (45) 7 (44)
RR and V , the standard deviations of delivered V s and RRs ACLS-certified
T
T
during each test were calculated. Further characterization of Yes 7 (35) 5 (31)
the variability during a given test was done with Poincaré No 13 (65) 11 (69)
plots of V and RR. Short-term, or cycle-to-cycle, variation BLS = basic life support; ACLS = advanced cardiovascular life support.
26
T
(SD1) is defined as the standard deviation perpendicular to
the line of identity. Long-term variation (SD2) is the remain- Delivered Tidal Volumes and Respiratory Rates
ing variation, parallel to the line of identity. Graphically, VTs and RRs More Closely Approached Target Values
SD1 and SD2 are shown as the minor and major axes of an with Audiovisual Feedback
ellipse. 27 Average absolute deviations from target tidal volume |ΔV |
T
were significantly reduced by BENGI (Figure 3 a–d), demon-
Statistics strating that BENGI improved participant accuracy when used
The two-tailed Wilcoxon signed rank test, Spearman rank to reach target V s. Similarly, average absolute deviations of
T
correlation coefficient, and Mann-Whitney U test were per- RRs delivered to the target |ΔRR| were significantly lower with
formed using Prism (version 9.3.1, GraphPad, San Diego, CA) BENGI (scenarios 1–3) or the use of BENGI plus metronome
and Levene’s test for equality of variances with SPSS (version (scenario 4, Figure 3 e–h). Conversely, BENGI use did not alter
Enhanced Manual Ventilation with a Handheld Audiovisual Device | 11