Page 12 - JSOM Fall 2024
P. 12
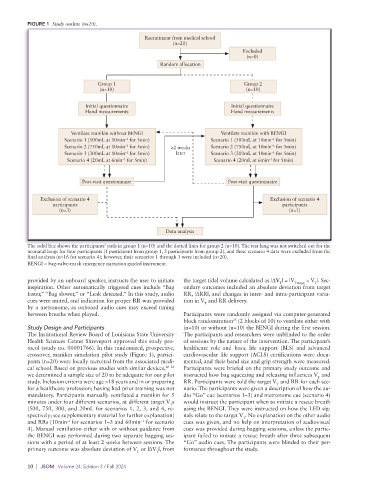
FIGURE 1 Study outline (n=20).
Recruitment from medical school
(n=20)
Excluded
(n=0)
Random allocation
Group 1 Group 2
(n=10) (n=10)
Initial questionnaire Initial questionnaire
Hand measurements Hand measurements
Ventilate manikin without BENGI Ventilate manikin with BENGI
Scenario 1 (500mL at 10min for 5min) Scenario 1 (500mL at 10min for 5min)
–1
–1
Scenario 2 (750mL at 10min for 5min) ≥2 weeks Scenario 2 (750mL at 10min for 5min)
–1
–1
Scenario 3 (300mL at 10min for 5min) later Scenario 3 (300mL at 10min for 5min)
–1
–1
Scenario 4 (20mL at 6min for 5min) Scenario 4 (20mL at 6min for 5min)
–1
–1
Post-visit questionnaire Post-visit questionnaire
Exclusion of scenario 4 Exclusion of scenario 4
participants participants
(n=3) (n=1)
Data analysis
The solid line shows the participants’ path in group 1 (n=10) and the dotted lines for group 2 (n=10). The test lung was not switched out for the
neonatal lungs for four participants (1 participant from group 1, 3 participants from group 2), and these scenario 4 data were excluded from the
final analysis (n=16 for scenario 4); however, their scenarios 1 through 3 were included (n=20).
BENGI = bag-valve-mask emergency narration guided instrument.
provided by an onboard speaker, instructs the user to initiate the target tidal volume calculated as |ΔV | = |V Ttarget − V |. Sec-
T
T
inspiration. Other automatically triggered cues include “Bag ondary outcomes included an absolute deviation from target
faster,” “Bag slower,” or “Leak detected.” In this study, audio RR, |ΔRR|, and changes in inter- and intra-participant varia-
cues were muted, and indication for proper RR was provided tion in V and RR delivery.
T
by a metronome, as onboard audio cues may exceed timing
between breaths when played. Participants were randomly assigned via computer-generated
25
block randomization (2 blocks of 10) to ventilate either with
Study Design and Participants (n=10) or without (n=10) the BENGI during the first session.
The Institutional Review Board of Louisiana State University The participants and researchers were unblinded to the order
Health Sciences Center Shreveport approved this study pro- of sessions by the nature of the intervention. The participant’s
tocol (study no. 00001766). In this randomized, prospective, healthcare role and basic life support (BLS) and advanced
crossover, manikin simulation pilot study (Figure 1), partici- cardiovascular life support (ACLS) certifications were docu-
pants (n=20) were locally recruited from the associated medi- mented, and their hand size and grip strength were measured.
cal school. Based on previous studies with similar devices, 20–22 Participants were briefed on the primary study outcome and
we determined a sample size of 20 to be adequate for our pilot instructed how bag squeezing and releasing influences V and
T
study. Inclusion criteria were age >18 years and in or preparing RR. Participants were told the target V and RR for each sce-
T
for a healthcare profession; having had prior training was not nario. The participants were given a description of how the au-
mandatory. Participants manually ventilated a manikin for 5 dio “Go” cue (scenarios 1–3) and metronome cue (scenario 4)
minutes under four different scenarios, at different target V s would instruct the participant when to initiate a rescue breath
T
(500, 750, 300, and 20mL for scenarios 1, 2, 3, and 4, re- using the BENGI. They were instructed on how the LED sig-
spectively; see supplementary material for further explanation) nals relate to the target V . No explanation on the other audio
T
and RRs (10min for scenarios 1–3 and 60min for scenario cues was given, and no help on interpretation of audiovisual
−1
−1
4). Manual ventilation either with or without guidance from cues was provided during bagging sessions, unless the partic-
the BENGI was performed during two separate bagging ses- ipant failed to initiate a rescue breath after three subsequent
sions with a period of at least 2 weeks between sessions. The “Go” audio cues. The participants were blinded to their per-
primary outcome was absolute deviation of V or |ΔV |, from formance throughout the study.
T T
10 | JSOM Volume 24, Edition 3 / Fall 2024