Page 40 - JSOM Fall 2021
P. 40
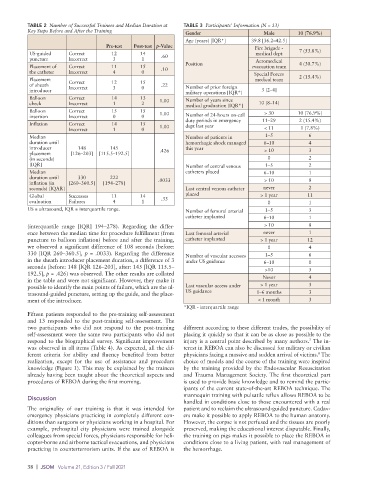
TABLE 2 Number of Successful Trainees and Median Duration at TABLE 3 Participants’ Information (N = 13)
Key Steps Before and After the Training Gender Male 10 (76.9%)
Age (years) [IQR*] 39.8 [36.2–42.5]
Pre-test Post-test p-Value Fire brigade -
US-guided Correct 12 14 medical dept 7 (53.8%)
puncture Incorrect 3 1 .60 Aeromedical
Placement of Correct 11 15 .10 Position evacuation team 4 (30.7%)
the catheter Incorrect 4 0 Special Forces
Placement Correct 12 15 medical team 2 (15.4%)
of sheath Incorrect 3 0 .22 Number of prior foreign
introducer military operations [IQR*] 3 [2–4]
Balloon Correct 14 13 1.00 Number of years since
check Incorrect 1 2 medical graduation [IQR*] 10 [8–14]
Balloon Correct 15 15 > 30 10 (76.9%)
insertion Incorrect 0 0 1.00 Number of 24-hours on-call
Inflation Correct 14 15 duty periods in emergency 11–29 2 (15.4%)
dept last year
Incorrect 1 0 1.00 < 11 1 (7.8%)
Median Number of patients in 1–5 6
duration until hemorrhagic shock managed 6–10 4
introducer 148 145 this year > 10 3
placement [126–203] [115.5–192.5] .426
(in seconds) 0 2
[IQR] Number of central venous 1–5 2
Median catheters placed 6–10 1
duration until 330 222 .0033 > 10 8
inflation (in [260–360.5] [194–278]
seconds) [IQAR] Last central venous catheter never 2
Global Successes 11 14 .33 placed > 1 year 11
evaluation Failures 4 1 0 1
US = ultrasound, IQR = interquartile range. Number of femoral arterial 1–5 3
catheter implanted 6–10 1
(interquartile range [IQR] 194–278). Regarding the differ- > 10 8
ence between the median time for procedure fulfillment (from Last femoral arterial never 1
puncture to balloon inflation) before and after the training, catheter implanted > 1 year 12
we observed a significant difference of 108 seconds (before: 0 4
330 [IQR 260–360.5], p = .0033). Regarding the difference Number of vascular accesses 1–5 6
in the sheath introducer placement duration, a difference of 3 under US guidance 6–10 0
seconds (before: 148 [IQR 126–203], after: 145 [IQR 115.5– >10 3
192.5], p = .426) was observed. The other results are collated
in the table and were not significant. However, they make it Never 4
possible to identify the main points of failure, which are the ul- Last vascular access under > 1 year 3
trasound-guided puncture, setting up the guide, and the place- US guidance 1–6 months 3
ment of the introducer. < 1 month 3
*IQR - interquartile range
Fifteen patients responded to the pre-training self-assessment
and 13 responded to the post-training self-assessment. The
two participants who did not respond to the post-training different according to these different trades, the possibility of
self-assessment were the same two participants who did not placing it quickly so that it can be as close as possible to the
7
respond to the biographical survey. Significant improvement injury is a central point described by many authors. The in-
was observed in all items (Table 4). As expected, all the dif- terest in REBOA can also be discussed for military or civilian
ferent criteria for ability and fluency benefited from better physicians facing a massive and sudden arrival of victims. The
8
realization, except for the use of assistance and procedure choice of models and the course of the training were inspired
knowledge (Figure 1). This may be explained by the trainees by the training provided by the Endovascular Resuscitation
already having been taught about the theoretical aspects and and Trauma Management Society. The first theoretical part
procedures of REBOA during the first morning. is used to provide basic knowledge and to remind the partic-
ipants of the current state-of-the-art REBOA technique. The
mannequin training with pulsatile reflux allows REBOA to be
Discussion
handled in conditions close to those encountered with a real
The originality of our training is that it was intended for patient and to reclaim the ultrasound-guided puncture. Cadav-
emergency physicians practicing in completely different con- ers make it possible to apply REBOA to the human anatomy.
ditions than surgeons or physicians working in a hospital. For However, the corpse is not perfused and the tissues are poorly
example, prehospital city physicians were trained alongside preserved, making the educational interest disputable. Finally,
colleagues from special forces, physicians responsible for heli- the training on pigs makes it possible to place the REBOA in
copter-borne and airborne tactical evacuations, and physicians conditions close to a living patient, with real management of
practicing in counterterrorism units. If the use of REBOA is the hemorrhage.
38 | JSOM Volume 21, Edition 3 / Fall 2021