Page 135 - JSOM Fall 2021
P. 135
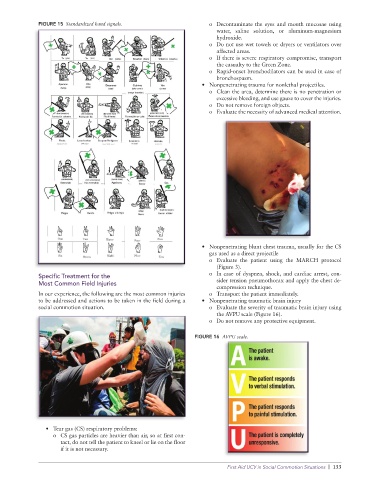
FIGURE 15 Standardized hand signals. o Decontaminate the eyes and mouth mucosae using
water, saline solution, or aluminum-magnesium
hydroxide.
o Do not use wet towels or dryers or ventilators over
affected areas.
o If there is severe respiratory compromise, transport
the casualty to the Green Zone.
o Rapid-onset bronchodilators can be used in case of
bronchospasm.
• Nonpenetrating trauma for nonlethal projectiles.
o Clean the area, determine there is no penetration or
excessive bleeding, and use gauze to cover the injuries.
o Do not remove foreign objects.
o Evaluate the necessity of advanced medical attention.
• Nonpenetrating blunt chest trauma, usually for the CS
gas used as a direct projectile
o Evaluate the patient using the MARCH protocol
(Figure 3).
o In case of dyspnea, shock, and cardiac arrest, con-
Specific Treatment for the sider tension pneumothorax and apply the chest de-
Most Common Field Injuries
compression technique.
In our experience, the following are the most common injuries o Transport the patient immediately.
to be addressed and actions to be taken in the field during a • Nonpenetrating traumatic brain injury
social commotion situation. o Evaluate the severity of traumatic brain injury using
the AVPU scale (Figure 16).
o Do not remove any protective equipment.
FIGURE 16 AVPU scale.
• Tear gas (CS) respiratory problems:
o CS gas particles are heavier than air, so at first con-
tact, do not tell the patient to kneel or lie on the floor
if it is not necessary.
First Aid UCV in Social Commotion Situations | 133