Page 40 - 2020 JSOM Winter
P. 40
APPENDIX F: EPINEPHRINE (NOREPINEPHRINE) – VASOPRESSOR GUIDE
Consider starting low-dose vasopressors—either epinephrine, ◆ Concentration: 10μg epiznephrine/mL
or norepinephrine if available—after 30mL/kg of IVF and no ◆ Onset: 1 minute
changes in MAP, urine output, or mentation. Epinephrine ◆ Duration: 5–10 minutes
1
can improve blood pressure by 1) vasoconstriction and 2) in- ◆ Dose: 0.5–2mL every 2–5 minutes (5–20μg)
creasing cardiac contractility, thus improving cardiac output.
2
Vaso pressors are rarely used outside of a critical care setting Administration: very slow IV push. 1mL/min for 10 minutes.
and use in an austere environment indicates a dire situation Rapid administration can cause rebound tachycardia, hyper-
and must be monitored extremely closely. The dose of either tensive emergency, and cardiac arrest.
epinephrine or norepinephrine are the same for drip calcu-
lations. Epinephrine is presented as it is far more available Epinephrine as a vasopressor drip: epinephrine 4μg/min bag
in austere practice settings. These are presented as low-dose reference chart. This dose is a starting/maintenance point in
starting points and any adjustments should be directly under the application of an epinephrine (vasopressor) IV drip bag—
telemedicine guidance. Of note: if monitoring, levels of lactate epinephrine challenge. Gold-standard hospital practice uti-
may rise with use of epinephrine as a vasopressor. lizes a central line for this intervention; however, in an austere
setting, peripheral antecubital access is acceptable (humeral,
Epinephrine, as an IV or IO push-dose: A 10mL syringe con- tibial, and sternal IO are also acceptable if flow rate can be
sisting of 9mL of normal saline (0.9% NaCl) with 1mL of precisely managed). The drip rate should be adjusted up, down
cardiac epinephrine (1:10,000 or 100μg/mL). Administer to or discontinued depending on the perfusion or vitals status of
acutely correct a blood pressure indicative of shock (systolic the patient. Once a vasopressor is started, the patient must be
<90). Administer a lower-end dose (0.5–1mL) while preparing constantly monitored. Whenever possible, telemedicine con-
a longer-term IVF drip (below). sultation is required when vasopressor support is initiated.
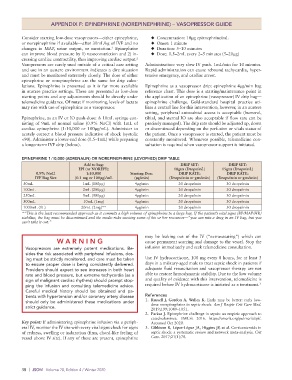
EPINEPHRINE 1:10,000 (ADRENALIN) OR NOREPINEPHRINE (LEVOPHED) DRIP TABLE
Add to bag: DRIP SET: DRIP SET:
EPI (or NOREPI): 10gtts (Drops/mL) 15gtts (Drops/mL)
0.9% NaCl 1:10,000 Starting Dose DRIP RATE: DRIP RATE:
IVF Bag Size (0.1 mg or 100μg)/mL (μg/min) (Drops/min or gtts/min) (Drops/min or gtts/min)
50mL 1mL (100μg) 4μg/min 20 drops/min 30 drops/min
100mL 2mL (200μg) 4μg/min 20 drops/min 30 drops/min
250mL 5mL (500μg) 4μg/min 20 drops/min 30 drops/min
500mL 10mL (1mg) 4μg/min 20 drops/min 30 drops/min
1000mL (1L) 20mL (2mg)** 4μg/min 20 drops/min 30 drops/min
**This is the least recommended approach as it commits a high volume of epinephrine to a large bag. If the patient’s vital signs (BP/MAP/HR)
stabilize, the bag must be discontinued and the medic risks wasting some of his or her resources—“you can mix a drug in an IV bag, but you
can’t take it out.”
may be leaking out of the IV (“extravasating”) which can
W ARNING cause permanent scarring and damage to the vessel. Stop the
Vasopressors are extremely potent medications. Be- infusion immediately and seek telemedicine consultation.
sides the risk associated with peripheral infusions, dos-
ing must be strictly monitored, and care must be taken Use IV hydrocortisone, 100 mg every 8 hours, for at least 3
to ensure proper dose is being consistently delivered. days in a military-aged male to treat septic shock in patients if
Providers should expect to see increases in both heart adequate fluid resuscitation and vasopressor therapy are not
rate and blood pressure, but extreme tachycardia (as a able to restore hemodynamic stability. Due to the low volume
sign of malignant cardiac rhythms) should prompt stop- and quality of evidence with this intervention, telemedicine is
ping the infusion and consulting telemedicine advice. required before IV hydrocortisone is initiated as a treatment. 3
Careful medical history should be obtained and pa-
tients with hypertension and/or coronary artery disease References
should only be administered these medications under 1. Russell J, Gordon A, Walley K. Early may be better: early low-
strict guidance. dose norepinephrine in septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
2019;199:1049–1051.
2. Farkas J. Epinephrine challenge in sepsis: an empiric approach to
catecholamines. EMCrit 2016. https://emcrit.org/pulmcrit/epi/.
Key point: If administering epinephrine infusion via a periph- Accessed Oct 2020.
eral IV, monitor the IV site with every vital signs check for signs 3. Gibbison B, López-López JA, Higgins JP, et al. Corticosteroids in
of redness, swelling or induration (firm, chord-like feeling of septic shock: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Crit
vessel above IV site). If any of these are present, epinephrine Care. 2017;21(1):78.
38 | JSOM Volume 20, Edition 4 / Winter 2020