Page 93 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Spring 2016
P. 93
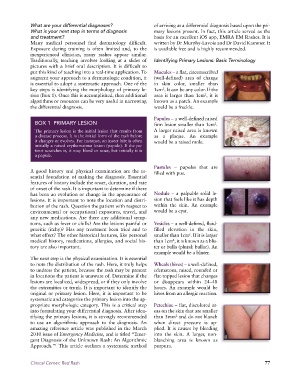
What are your differential diagnoses? of arriving at a differential diagnosis based upon the pri-
What is your next step in terms of diagnosis mary lesions present. In fact, this article served as the
and treatment? basis for an excellent iOS app, EMRA EM Rashes. It is
Many medical personnel find dermatology difficult. written by Dr Murphy-Lavoie and Dr David Kammer. It
Exposure during training is often limited and, to the is available free and is highly recommended.
inexperienced clinician, many rashes appear similar.
Traditionally, teaching involves looking at a slides of Identifying Primary Lesions: Basic Terminology
pictures with a brief oral description. It is difficult to
put this kind of teaching into a real-time application. To Macules – a flat, circumscribed
augment your approach to a dermatologic condition, it (well-defined) area of change
is essential to adopt a systematic approach. One of the in skin color, smaller than
key steps is identifying the morphology of primary le- 1cm . It can be any color. If the
2
sion (Box 1). Once this is accomplished, then additional area is larger than 1cm , it is
2
algorithms or resources can be very useful in narrowing known as a patch. An example
the differential diagnosis. would be a freckle.
Papules – a well-defined raised
BOX 1 PRIMARY LESION firm lesion smaller than 1cm .
2
The primary lesion is the initial lesion that results from A larger raised area is known
a disease process. It is the initial form of the rash before as a plaque. An example
it changes or evolves. For instance, an insect bite is often would be a raised mole.
initially a raised erythematous lesion (papule). If the pa-
tient scratches it, it may bleed or ooze, but initially it is
a papule.
Pustules – papules that are
A good history and physical examination are the es- filled with pus.
sential foundation of making the diagnosis. Essential
features of history include the onset, duration, and rate
of onset of the rash. It is important to determine if there
has been an evolution or change in the appearance of Nodule – a palpable solid le-
lesions. It is important to note the location and distri- sion that feels like it has depth
bution of the rash. Question the patient with respect to within the skin. An example
environmental or occupational exposures, travel, and would be a cyst.
any new medications. Are there any additional symp-
toms, such as fever or chills? Are the lesions painful or Vesicles – a well-defined, fluid-
pruritic (itchy)? Has any treatment been tried and to filled elevation in the skin,
what effect? The other historical features, like personal smaller than 1cm . If it is larger
2
medical history, medications, allergies, and social his- than 1cm , it is known as a blis-
2
tory are also important. ter or bulla (plural: bullae). An
example would be a blister.
The next step is the physical examination. It is essential
to note the distribution of the rash. Here, it truly helps Wheals (hives) – a well-defined,
to undress the patient, because the rash may be present edematous, raised, rounded or
in locations the patient is unaware of. Determine if the flat-topped lesion that changes
lesions are localized, widespread, or if they only involve or disappears within 24–48
the extremities or trunk. It is important to identify the hours. An example would be
original or primary lesion. Here, it is important to be hives from an allergic reaction.
systematic and categorize the primary lesion into the ap-
propriate morphologic category. This is a critical step Petechiae – flat, discolored ar-
into formulating your differential diagnosis. After iden- eas on the skin that are smaller
tifying the primary lesions, it is strongly recommended than 3mm and do not blanch
2
to use an algorithmic approach to the diagnosis. An when direct pressure is ap-
amazing reference article was published in the March plied. It is causes by bleeding
2010 issue of Emergency Medicine, and is titled “Emer- into the skin. A larger, non-
gent Diagnosis of the Unknown Rash: An Algorithmic blanching area is known as
Approach.” This article outlines a systematic method purpura.
1
Clinical Corner: Red Rash 77