Page 61 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Spring 2014
P. 61
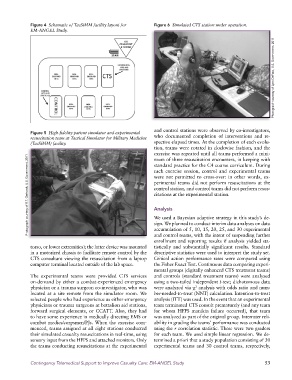
Figure 4 Schematic of TacSiMM facility layout for Figure 6 Simulated CTS station under operation.
EM-ANGEL Study.
Photograph courtesy of Lynn DeFato, U.S. Government, 2011
and control stations were observed by co-investigators,
Figure 5 High-fidelity patient simulator and experimental
resuscitation team at Tactical Simulator for Military Medicine who documented completion of interventions and re-
(TacSiMM) facility. spective elapsed times. At the completion of each evolu-
tion, teams were rotated in clockwise fashion, and the
exercise was repeated until all teams performed a mini-
Photograph courtesy of R.T. Gerhardt, U.S. Government, 2011 were not permitted to cross-over: in other words, ex-
mum of three resuscitation encounters, in keeping with
standard practice for the C4 course curriculum. During
each exercise session, control and experimental teams
perimental teams did not perform resuscitations at the
control station, and control teams did not perform resus-
citations at the experimental station.
Analysis
We used a Bayesian adaptive strategy in this study’s de-
sign. We planned to conduct interim data analyses on data
accumulation of 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 experimental
and control teams, with the intent of suspending further
enrollment and reporting results if analysis yielded sta-
torso, or lower extremities); the latter device was mounted tistically and substantially significant results. Standard
in a motorized chassis to facilitate remote control by the descriptive statistics were used to interpret the study set.
CTS consultant viewing the resuscitation from a laptop Critical action performance rates were compared using
computer terminal located outside of the lab space. the Fisher Exact Test. Continuous data comparing experi-
mental groups (digitally enhanced CTS treatment teams)
The experimental teams were provided CTS services and controls (standard treatment teams) were analyzed
on-demand by either a combat-experienced emergency using a two-tailed independent t-test; dichotomous data
physician or a trauma surgeon co-investigator, who was were analyzed via χ analysis with odds ratio and num-
2
located at a site remote from the simulator room. We ber-needed-to-treat (NNT) calculation. Intention-to-treat
selected people who had experience as either emergency analysis (ITT) was used. In the event that an experimental
physicians or trauma surgeons at battalion aid stations, team terminated CTS consult prematurely (and any team
forward surgical elements, or CCATT. Also, they had for whom HFPS manikin failure occurred), that team
to have some experience in medically directing EMS or was analyzed as part of the original group. Interrater reli-
combat medics/corpsmen/PJs. When the exercise com- ability in grading the teams’ performance was conducted
menced, teams assigned at all eight stations conducted using the r correlation statistic. There were two graders
their simulated casualty resuscitations in real-time, using for each team. We used simple linear regression. We de-
sensory input from the HFPS and attached monitors. Only termined a priori that a study population consisting of 30
the teams conducting resuscitations at the experimental experimental teams and 30 control teams, respectively,
Contingency Telemedical Support to Improve Casualty Care: EM-ANGEL Study 53