Page 75 - JSOM Spring 2024
P. 75
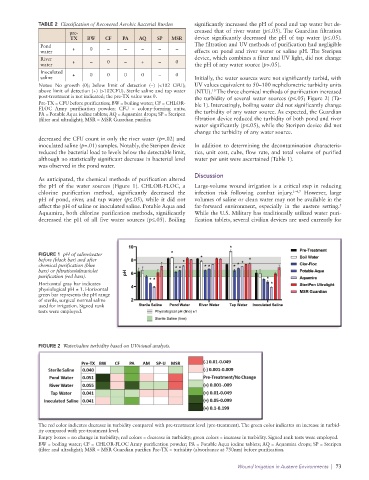
TABLE 2 Classification of Recovered Aerobic Bacterial Burden significantly increased the pH of pond and tap water but de-
pre- creased that of river water (p≤.05). The Guardian filtration
TX BW CF PA AQ SP MSR device significantly decreased the pH of tap water (p≤.05).
Pond The filtration and UV methods of purification had negligible
water + 0 – – – – – effects on pond and river water or saline pH. The Steripen
River device, which combines a filter and UV light, did not change
water + – 0 – + – 0 the pH of any water source (p>.05).
Inoculated + 0 0 0 0 – 0
saline Initially, the water sources were not significantly turbid, with
Notes: No growth (0); below limit of detection (–) (<102 CFU); UV values equivalent to 50–100 nephelometric turbidity units
above limit of detection (+) (>102CFU). Sterile saline and tap water (NTU). The three chemical methods of purification increased
10
post-treatment is not indicated; the pre-TX value was 0. the turbidity of several water sources (p≤.05; Figure 2) (Ta-
Pre-TX = CFU before purification; BW = boiling water; CF = CHLOR- ble 1). Interestingly, boiling water did not significantly change
FLOC Army purification powder; CFU = colony-forming units;
PA = Potable Aqua iodine tablets; AQ = Aquamira drops; SP = Steripen the turbidity of any water source. As expected, the Guardian
(filter and ultralight); MSR = MSR Guardian purifier. filtration device reduced the turbidity of both pond and river
water significantly (p≤.05), while the Steripen device did not
change the turbidity of any water source.
decreased the CFU count in only the river water (p=.02) and
inoculated saline (p=.01) samples. Notably, the Steripen device In addition to determining the decontamination characteris-
reduced the bacterial load to levels below the detectable limit, tics, unit cost, cube, flow rate, and total volume of purified
although no statistically significant decrease in bacterial level water per unit were ascertained (Table 1).
was observed in the pond water.
Discussion
As anticipated, the chemical methods of purification altered
the pH of the water sources (Figure 1). CHLOR-FLOC, a Large-volume wound irrigation is a critical step in reducing
chlorine purification method, significantly decreased the infection risk following combat injury. 1–4,7 However, large
pH of pond, river, and tap water (p≤.05), while it did not volumes of saline or clean water may not be available in the
5
affect the pH of saline or inoculated saline. Potable Aqua and far-forward environment, especially in the austere setting.
Aquamira, both chlorine purification methods, significantly While the U.S. Military has traditionally utilized water puri-
decreased the pH of all five water sources (p≤.05). Boiling fication tablets, several civilian devices are used currently for
FIGURE 1 pH of saline/water
before (black bar) and after
chemical purification (blue
bars) or filtration/ultraviolet
purification (red bars).
Horizontal gray bar indicates
physiological pH ± 1. Horizontal
green bar represents the pH range
of sterile, surgical normal saline
used for irrigation. Signed rank
tests were employed.
FIGURE 2 Water/saline turbidity based on UV/visual analysis.
The red color indicates decrease in turbidity compared with pre-treatment level (pre-treatment). The green color indicates an increase in turbid-
ity compared with pre-treatment level.
Empty boxes = no change in turbidity; red colors = decrease in turbidity; green colors = increase in turbidity. Signed rank tests were employed.
BW = boiling water; CF = CHLOR-FLOC Army purification powder; PA = Potable Aqua iodine tablets; AQ = Aquamira drops; SP = Steripen
(filter and ultralight); MSR = MSR Guardian purifier. Pre-TX = turbidity (absorbance at 750nm) before purification.
Wound Irrigation in Austere Environments | 73