Page 107 - JSOM Fall 2018
P. 107
FIGURE 2 Bloom’s taxonomy. 3 weeks), Clinical Medicine (5 weeks), Prolonged Field Care (2
weeks), Field Training Exercise (1 week), Tactical Emergency
Casualty Care (TECC) and Tactical Paramedic Certification (1
week), and Clinical Hospital Rotations (2 weeks).
Module 1: Basic Medical Science
The Basic Medical Science module begins with an overview
of biochemistry, cell structure, and the major organ systems
in the human body including the circulatory, respiratory, di
gestive, lymphatic, urologic, nervous, reproductive, integu
mentary, musculoskeletal, and endocrine systems. A Basic Life
Support class is also covered at the end of the second week.
The NSOCM student should be at least AMFR qualified, but
adding two additional weeks (for a total of 24 weeks) to the
2018–2019 NSOCM course during this module will assure a
baseline level of knowledge is achieved. The last week of Ba
sic Medical Science covers pharmacology principles (kinetic
and dynamic), dosage, drip rates, and administration routes
of medications.
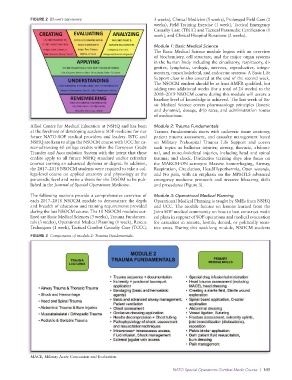
Allied Centre for Medical Education at NSHQ and has been Module 2: Trauma Fundamentals
at the forefront of developing academic SOF medicine for our Trauma Fundamentals starts with cadaveric tissue anatomy,
future NATOSOF medical providers and leaders. ISTC and patient trauma assessment, and casualty management based
NSHQ are keen to align the NSOCM course with UCC for ca on Military Prehospital Trauma Life Support and covers
reeradvancing 60 college credits within the European Credit such topics as ballistics injuries; airway, thoracic, abdomi
Transfer and Accumulation System with the intent that these nal, and musculoskeletal injuries, including head and spinal
credits apply to all future NSHQ standard and/or refresher trauma; and shock. Distinctive training days also focus on
courses earning an advanced diploma or degree. In addition, the MARCHON acronym: Massive hemorrhaging, Airway,
the 2017–2018 NSOCM students were required to take a col Respiration, Circulation, Head/Hypothermia, Open wounds,
legelevel course on applied anatomy and physiology at the and No pain, with an emphasis on the MPHTLS advanced
paramedic level and write a thesis for the DiSOM to be pub emergency medicine protocols and invasive lifesaving skills
lished in the Journal of Special Operations Medicine. and procedures (Figure 3).
The following sections provide a comprehensive overview of Module 3: Operational Medical Planning
each 2017–2018 NSOCM module to demonstrate the depth Operational Medical Planning is taught by SMEs from NSHQ
and breadth of education and training requirements provided and UCC. The module focuses on lessons learned from the
during the last NSOCM course. The 10 NSOCM modules out Joint SOF medical community on how to best construct medi
lined are Basic Medical Sciences (3 weeks), Trauma Fundamen cal plans in support of SOF operations and medical evacuation
tals (3 weeks), Operational Medical Planning (1 week), Rescue for casualties in remote, hostile, denied, or politically sensi
Techniques (1 week), Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC; tive areas. During this weeklong module, NSOCM students
FIGURE 3 Components of module 2: Trauma Fundamentals.
MACE, Military Acute Concussion and Evaluation.
NATO Special Operations Combat Medic Course | 105