Page 32 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Spring 2017
P. 32
there were no operating room or surgical specialists
within the region. The only medical treatment provided
was the insertion of a Foley catheter because the patient
continued having difficulty urinating.
This case and photographs of the patient were forwarded
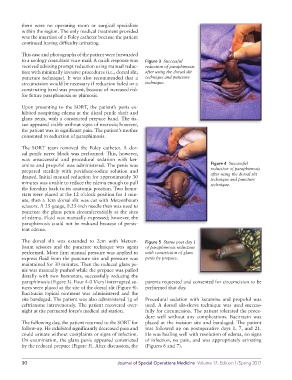
to a urology consultant via e-mail. A quick response was Figure 3 Successful
received advising prompt reduction using manual reduc- reduction of paraphimosis
tion with minimally invasive procedures (i.e., dorsal slit, after using the dorsal slit
puncture technique). It was also recommended that a technique and puncture
circumcision would be necessary if reduction failed or a technique.
constricting band was present, because of increased risk
for future paraphimosis or phimosis.
Upon presenting to the SORT, the patient’s penis ex-
hibited nonpitting edema at the distal penile shaft and
glans penis, with a constricted prepuce band. The tis-
sue appeared viable without signs of necrosis; however,
the patient was in significant pain. The patient’s mother
consented to reduction of paraphimosis.
The SORT team removed the Foley catheter. A dor-
sal penile nerve block was performed. This, however,
was unsuccessful and procedural sedation with ket-
amine and propofol was administered. The penis was Figure 4 Successful
prepared sterilely with povidone-iodine solution and reduction of paraphimosis
after using the dorsal slit
draped. Initial manual reduction for approximately 30 technique and puncture
minutes was unable to reduce the edema enough to pull technique.
the foreskin back to its anatomic position. Two hemo-
stats were placed at the 12 o’clock position for 1 min-
ute, then a 1cm dorsal slit was cut with Metzenbaum
scissors. A 25-gauge, 0.25-inch needle then was used to
puncture the glans penis circumferentially at the sites
of edema. Fluid was manually expressed; however, the
paraphimosis could not be reduced because of persis-
tent edema.
The dorsal slit was extended to 2cm with Metzen- Figure 5 Status post day 1
baum scissors and the puncture technique was again of paraphimosis reduction
performed. More firm manual pressure was applied to with constriction of glans
express fluid from the puncture site and pressure was penis by prepuce.
maintained for 30 minutes. Then the reduced glans pe-
nis was manually pushed while the prepuce was pulled
distally with two hemostats, successfully reducing the
paraphimosis (Figure 3). Four 4-0 Vicryl interrupted su- parents requested and consented for circumcision to be
tures were placed at the site of the dorsal slit (Figure 4). performed that day.
Bacitracin topical ointment was administered and the
site bandaged. The patient was also administered 1g of Procedural sedation with ketamine and propofol was
ceftriaxone intravenously. The patient recovered over- used. A dorsal slit-sleeve technique was used success-
night at the partnered force’s medical aid station. fully for circumcision. The patient tolerated the proce-
dure well without any complications. Bacitracin was
The following day, the patient returned to the SORT for placed at the incision site and bandaged. The patient
follow-up. He exhibited significantly decreased pain and was followed up on postoperative days 1, 7, and 21.
could urinate without complaints or signs of infection. He was healing well with resolution of edema, no signs
On examination, the glans penis appeared constricted of infection, no pain, and was appropriately urinating
by the reduced prepuce (Figure 5). After discussion, the (Figures 6 and 7).
10 Journal of Special Operations Medicine Volume 17, Edition 1/Spring 2017