Page 120 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Summer 2015
P. 120
Chronic Q fever, which is the result in less than 5% the first nucleic acid amplification test for military per-
of those who have been acutely infected, may occur sonnel serving overseas, to be used in the Joint Biological
months to years after the initial illness. The hallmark of Agency Identification and Diagnostic System (JBAIDS).
this disease in adults is “culture negative” endocarditis, Polymerase chain reaction testing is useful early in the
especially in those with preexisting heart valve disease, course of the illness before a rise in antibody titer and
vascular grafts, and arterial aneurysms. This disease is within the first 1 to 2 days after the initiation of appro-
fatal in most cases, if left untreated (Figure 2). priate antibiotics. Chronic Q fever is diagnosed serolog-
ically in conjunction with evaluation by a cardiologist
for evidence of endocarditis.
Diagnosis
The single most important element in making the diag- Vaccination and Treatment
nosis of acute Q fever is including it in the differential
diagnosis. The diagnosis is reliably made serologically A vaccine against Q fever is in use in Australia, but is
through an indirect immunofluorescence assay compari- not available for commercial use in the United States.
son of acute and convalescent phase immunoglobulin G
in serum samples drawn 3 to 6 weeks apart. A single, el- The mainstay of treatment for Q fever is doxycycline in
evated convalescent sample is the most common means both adults and children and in both acute and chronic
of diagnosis of cases in the United States, as the disease disease. It should be started prior to laboratory confir-
is not often considered while the patient is acutely ill. In mation (Table 1). Treatment is most effective if started
2011, the US Food and Drug Administration approved within the first 3 days of the illness.
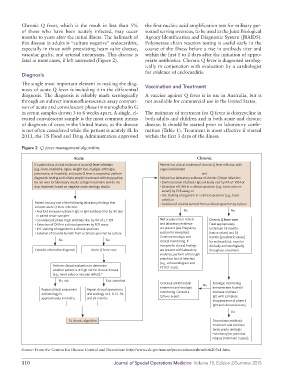
Figure 2 Q fever management algorithm.
Acute Chronic
If a patient has clinical evidence of acute Q fever infection Patient has clinical evidence of chronic Q fever infection with
(e.g., fever, headache, rigors, weight loss, myalgia, arthralgia, organ involvement
pneumonia, or hepatitis), and acute Q fever is suspected, perform and
diagnostic testing and initiate empiric treatment with doxycycline. Patient has laboratory evidence of chronic Q fever infection:
Do not wait for laboratory results to begin treatment and do not • Demonstration of phase I IgG antibody titer by IFA ≥1:1024 or
stop treatment based on negative acute serology results. • Detection of DNA in a clinical specimen (e.g., heart valve or
serum) by PCR assay; or
• IHC staining of organism in a clinical specimen (e.g., heart
valve); or
Patient has any one of the following laboratory findings that • Isolation of Coxiella burnetii from a clinical specimen by culture
indicate acute Q fever infection:
• Fourfold increase in phase II IgG or IgM antibody titer by IFA test No Yes
in paired serum samples
• Convalescent phase II IgG antibody titer by IFA of ≥ 1:128 Not a case unless clinical Chronic Q fever case
• Detection of DNA in a clinical specimen by PCR assay and laboratory evidence Treat appropriately
• IHC staining of organism in a clinical specimen are present (see Pregnancy (minimum 18 months
• Isolation of Coxiella burnetii from a clinical specimen by culture section for exception). [native valves] and 24
Continue serologic and months [prosthetic valves]
No Yes clinical monitoring. If for endocarditis); monitor
nonspecific clinical findings clinically and serologically
Consider alternative diagnosis Acute Q fever case are present with laboratory throughout treatment.
evidence, perform a thorough
search for foci of infection
(e.g., echocardiogram and
Perform clinical evaluation to determine PET/CT scan).
whether patient is at high risk for chronic disease
(e.g., heart value or vascular defect).*
No risk Risk identified
Continue antimicrobial Serologic monitoring
treatment and serologic No demonstrates fourfold
Repeat clinical assessment Repeat clinical assessment
and serology in and serology at 3, 6, 12, 18, monitoring. Consult a decrease in phase I
approximately 6 months. and 24 months. Q fever expert. IgG with complete
disappearance of phase II
IgM and clinical recovery.
Yes
To chronic algorithm Discontinue antibiotic
treatment and continue
twice yearly serologic
monitoring for potential
relapse (minimum 5 years).
Source: From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr6203a1.htm.
110 Journal of Special Operations Medicine Volume 15, Edition 2/Summer 2015