Page 46 - JSOM Spring 2024
P. 46
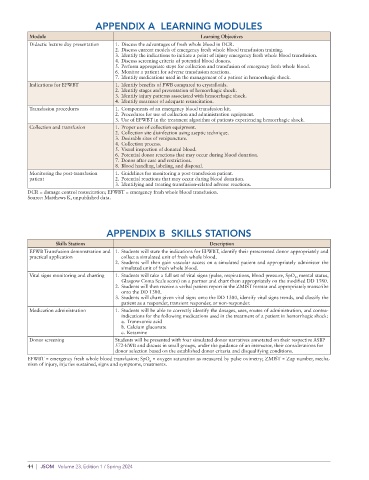
APPENDIX A LEARNING MODULES
Module Learning Objectives
Didactic lecture day presentation 1. Discuss the advantages of fresh whole blood in DCR.
2. Discuss current models of emergency fresh whole blood transfusion training.
3. Identify the indications to initiate a point of injury emergency fresh whole blood transfusion.
4. Discuss screening criteria of potential blood donors.
5. Perform appropriate steps for collection and transfusion of emergency fresh whole blood.
6. Monitor a patient for adverse transfusion reactions.
7. Identify medications used in the management of a patient in hemorrhagic shock.
Indications for EFWBT 1. Identify benefits of FWB compared to crystalloids.
2. Identify stages and presentation of hemorrhagic shock.
3. Identify injury patterns associated with hemorrhagic shock.
4. Identify measures of adequate resuscitation.
Transfusion procedures 1. Components of an emergency blood transfusion kit.
2. Procedures for use of collection and administration equipment.
3. Use of EFWBT in the treatment algorithm of patients experiencing hemorrhagic shock.
Collection and transfusion 1. Proper use of collection equipment.
2. Collection site disinfection using aseptic technique.
3. Desirable sites of venipuncture.
4. Collection process.
5. Visual inspection of donated blood.
6. Potential donor reactions that may occur during blood donation.
7. Donor after care and restrictions.
8. Blood handling, labeling, and disposal.
Monitoring the post-transfusion 1. Guidelines for monitoring a post-transfusion patient.
patient 2. Potential reactions that may occur during blood donation.
3. Identifying and treating transfusion-related adverse reactions.
DCR = damage control resuscitation; EFWBT = emergency fresh whole blood transfusion.
Source: Matthews K, unpublished data.
APPENDIX B SKILLS STATIONS
Skills Stations Description
EFWB Transfusion demonstration and 1. Students will state the indications for EFWBT, identify their prescreened donor appropriately and
practical application collect a simulated unit of fresh whole blood.
2. Students will then gain vascular access on a simulated patient and appropriately administer the
simulated unit of fresh whole blood.
Vital signs monitoring and charting 1. Students will take a full set of vital signs (pulse, respirations, blood pressure, SpO 2 , mental status,
Glasgow Coma Scale score) on a partner and chart them appropriately on the modified DD 1380.
2. Students will then receive a verbal patient report in the ZMIST format and appropriately transcribe
onto the DD 1380.
3. Students will chart given vital signs onto the DD 1380, identify vital signs trends, and classify the
patient as a responder, transient responder, or non-responder.
Medication administration 1. Students will be able to correctly identify the dosages, uses, routes of administration, and contra-
indications for the following medications used in the treatment of a patient in hemorrhagic shock:
a. Tranexamic acid
b. Calcium gluconate
c. Ketamine
Donor screening Students will be presented with four simulated donor narratives annotated on their respective ASBP
572-EWB and discuss in small groups, under the guidance of an instructor, their considerations for
donor selection based on the established donor criteria and disqualifying conditions.
EFWBT = emergency fresh whole blood transfusion; SpO = oxygen saturation as measured by pulse oximetry; ZMIST = Zap number, mecha-
2
nism of injury, injuries sustained, signs and symptoms, treatments.
44 | JSOM Volume 23, Edition 1 / Spring 2024