Page 43 - JSOM Spring 2024
P. 43
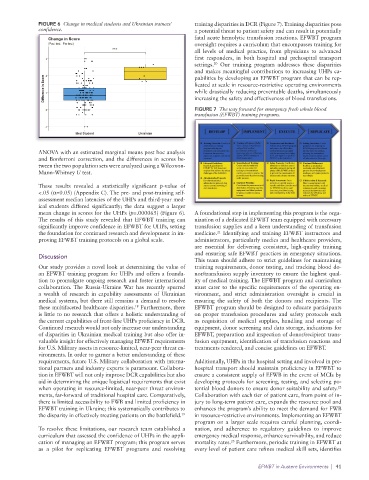
FIGURE 6 Change in medical students and Ukrainian trainees’ training disparities in DCR (Figure 7). Training disparities pose
confidence. a potential threat to patient safety and can result in potentially
fatal acute hemolytic transfusion reactions. EFWBT program
oversight requires a curriculum that encompasses training for
all levels of medical practice, from physicians to advanced
first responders, in both hospital and prehospital transport
20
settings. Our training program addresses these disparities
and makes meaningful contributions to increasing UHPs ca-
pabilities by developing an EFWBT program that can be rep-
licated at scale in resource-restrictive operating environments
while drastically reducing preventable deaths, simultaneously
increasing the safety and effectiveness of blood transfusions.
FIGURE 7 The way forward for emergency fresh whole blood
transfusion (EFWBT) training programs.
ANOVA with an estimated marginal means post hoc analysis
and Bonferroni correction, and the differences in scores be-
tween the two population sets were analyzed using a Wilcoxon-
Mann-Whitney U test.
These results revealed a statistically significant p-value of
<.05 (α=0.05) (Appendix C). The pre- and post-training self-
assessment median latencies of the UHPs and third-year med-
ical students differed significantly; the data suggest a larger
mean change in scores for the UHPs (p=.000065) (Figure 6). A foundational step in implementing this program is the orga-
The results of this study revealed that EFWBT training can nization of a dedicated EFWBT team equipped with necessary
significantly improve confidence in EFWBT for UHPs, setting transfusion supplies and a keen understanding of transfusion
21
the foundation for continued research and development in im- medicine. Identifying and training EFWBT instructors and
proving EFWBT training protocols on a global scale. administrators, particularly medics and healthcare providers,
are essential for delivering consistent, high-quality training
and ensuring safe EFWBT practices in emergency situations.
Discussion
This team should adhere to strict guidelines for maintaining
Our study provides a novel look at determining the value of training requirements, donor testing, and tracking blood do-
an EFWBT training program for UHPs and offers a founda- nor/transfusion supply inventory to ensure the highest qual-
tion to promulgate ongoing research and foster international ity of medical training. The EFWBT program and curriculum
collaboration. The Russia-Ukraine War has recently spurred must cater to the specific requirements of the operating en-
a wealth of research in capability assessments of Ukrainian vironment, and strict administration oversight is crucial in
medical systems, but there still remains a demand to resolve ensuring the safety of both the donors and recipients. The
these multifaceted healthcare disparities. Furthermore, there EFWBT program should be designed to educate participants
18
is little to no research that offers a holistic understanding of on proper transfusion procedures and safety protocols such
the current capabilities of front-line UHPs proficiency in DCR. as requisition of medical supplies, handling and storage of
Continued research would not only increase our understanding equipment, donor screening and data storage, indications for
of disparities in Ukrainian medical training but also offer in- EFWBT, preparation and inspection of donor/recipient trans-
valuable insight for effectively managing EFWBT requirements fusion equipment, identification of transfusion reactions and
for U.S. Military assets in resource-limited, near-peer threat en- treatments rendered, and concise guidelines on EFWBT.
vironments. In order to garner a better understanding of these
requirements, future U.S. Military collaboration with interna- Additionally, UHPs in the hospital setting and involved in pre-
tional partners and industry experts is paramount. Collabora- hospital transport should maintain proficiency in EFWBT to
tion in EFWBT will not only improve DCR capabilities but also ensure a consistent supply of EFWB in the event of MCIs by
aid in determining the unique logistical requirements that exist developing protocols for screening, testing, and selecting po-
when operating in resource-limited, near-peer threat environ- tential blood donors to ensure donor suitability and safety.
22
ments, far-forward of traditional hospital care. Comparatively, Collaboration with each tier of patient care, from point of in-
there is limited accessibility to FWB and limited proficiency in jury to long-term patient care, expands the resource pool and
EFWBT training in Ukraine; this systematically contributes to enhances the program’s ability to meet the demand for FWB
the disparity in effectively treating patients on the battlefield. 19 in resource-restrictive environments. Implementing an EFWBT
program on a larger scale requires careful planning, coordi-
To resolve these limitations, our research team established a nation, and adherence to regulatory guidelines to improve
curriculum that assessed the confidence of UHPs in the appli- emergency medical response, enhance survivability, and reduce
23
cation of managing an EFWBT program; this program serves mortality rates. Furthermore, periodic training in EFWBT at
as a pilot for replicating EFWBT programs and resolving every level of patient care refines medical skill sets, identifies
EFWBT in Austere Environments | 41