Page 37 - JSOM Fall 2023
P. 37
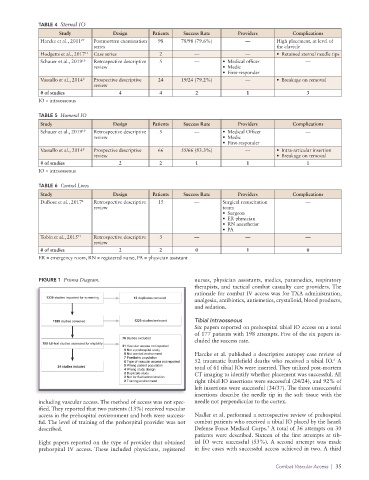
TABLE 4 Sternal IO
Study Design Patients Success Rate Providers Complications
Harcke et al., 2011 27 Postmortem examination 98 78/98 (79.6%) — High placement, at level of
series the clavicle
Hodgetts et al., 2017 13 Case series 2 — — • Retained sternal needle tips
Schauer et al., 2019 10 Retrospective descriptive 5 — • Medical officer —
review • Medic
• First-responder
Vassallo et al., 2014 8 Prospective descriptive 24 19/24 (79.2%) — • Breakage on removal
review
# of studies 4 4 2 1 3
IO = intraosseous
TABLE 5 Humeral IO
Study Design Patients Success Rate Providers Complications
Schauer et al., 2019 10 Retrospective descriptive 5 — • Medical Officer —
review • Medic
• First-responder
Vassallo et al., 2014 8 Prospective descriptive 66 55/66 (83.3%) — • Intra-articular insertion
review • Breakage on removal
# of studies 2 2 1 1 1
IO = intraosseous
TABLE 6 Central Lines
Study Design Patients Success Rate Providers Complications
DuBose et al., 2017 4 Retrospective descriptive 15 — Surgical resuscitation —
review team:
• Surgeon
• ER physician
• RN anesthetist
• PA
Tobin et al., 2015 11 Retrospective descriptive 3 — — —
review
# of studies 2 2 0 1 0
ER = emergency room, RN = registered nurse, PA = physician assistant
FIGURE 1 Prisma Diagram. nurses, physician assistants, medics, paramedics, respiratory
therapists, and tactical combat casualty care providers. The
rationale for combat IV access was for TXA administration,
10 duplicates removed
analgesia, antibiotics, antiemetics, crystalloid, blood products,
and sedation.
1229 studies irrelevant Tibial Intraosseous
Six papers reported on prehospital tibial IO access on a total
of 177 patients with 198 attempts. Five of the six papers in-
76 studies excluded
cluded the success rate.
31 Vascular access not reported
9 Not a prehospital study
8 Not combat environment Harcke et al. published a descriptive autopsy case review of
7 Paediatric population
6
6 Type of vascular access not reported 52 traumatic battlefield deaths who received a tibial IO. A
5 Wrong patient population
4 Wrong study design total of 61 tibial IOs were inserted. They utilized post-mortem
2 Duplicate study CT imaging to identify whether placement was successful. All
2 Not for fluid administration
2 Training environment right tibial IO insertions were successful (24/24), and 92% of
left insertions were successful (34/37). The three unsuccessful
insertions describe the needle tip in the soft tissue with the
including vascular access. The method of access was not spec- needle not perpendicular to the cortex.
ified. They reported that two patients (13%) received vascular
access in the prehospital environment and both were success- Nadler et al. performed a retrospective review of prehospital
ful. The level of training of the prehospital provider was not combat patients who received a tibial IO placed by the Israeli
7
described. Defense Force Medical Corps. A total of 36 attempts on 30
patients were described. Sixteen of the first attempts at tib-
Eight papers reported on the type of provider that obtained ial IO were successful (53%). A second attempt was made
prehospital IV access. These included physicians, registered in five cases with successful access achieved in two. A third
Combat Vascular Access | 35