Page 38 - 2022 Spring JSOM
P. 38
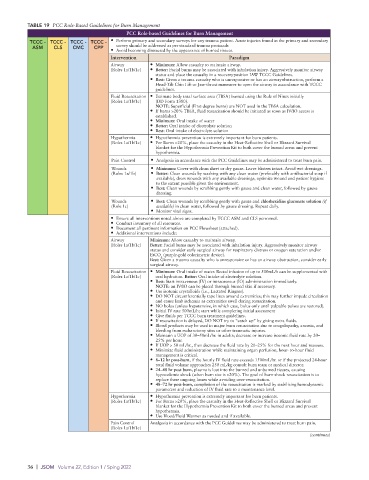
TABLE 19 PCC Role-Based Guidelines for Burn Management
PCC Role-based Guidelines for Burn Management
TCCC - TCCC - TCCC - TCCC - • Perform primary and secondary surveys for any trauma patient. Acute injuries found in the primary and secondary
ASM CLS CMC CPP survey should be addressed as per standard trauma protocols
• Avoid becoming distracted by the appearance of burned tissues.
Intervention Paradigm
Airway • Minimum: Allow casualty to maintain airway.
(Roles 1a/1b/1c) • Better: Facial burns may be associated with inhalation injury. Aggressively monitor airway
status and place the casualty in a recovery position IAW TCCC Guidelines.
• Best: Given a trauma casualty who is unresponsive or has an airway obstruction, perform a
Head-Tilt Chin Lift or Jaw-thrust maneuver to open the airway in accordance with TCCC
guidelines.
Fluid Resuscitation • Estimate body total surface area (TBSA) burned using the Rule of Nines initially
(Roles 1a/1b/1c) (DD Form 1380).
NOTE: Superficial (First-degree burns) are NOT used in the TBSA calculation.
• If burns >20% TBSA, fluid resuscitation should be initiated as soon as IV/IO access is
established.
• Minimum: Oral intake of water
• Better: Oral intake of electrolyte solution
• Best: Oral intake of electrolyte solution
Hypothermia • Hypothermia prevention is extremely important for burn patients.
(Roles 1a/1b/1c) • For Burns >20%, place the casualty in the Heat-Reflective Shell or Blizzard Survival
blanket for the Hypothermia Prevention Kit to both cover the burned areas and prevent
hypothermia.
Pain Control • Analgesia in accordance with the PCC Guidelines may be administered to treat burn pain.
Wounds • Minimum: Cover with clean sheet or dry gauze. Leave blisters intact. Avoid wet dressings.
(Roles 1a/1b) • Better: Clean wounds by washing with any clean water (preferably with antibacterial soap if
available), dress wounds with any available dressings; optimize wound and patient hygiene
to the extent possible given the environment.
• Best: Clean wounds by scrubbing gently with gauze and clean water, followed by gauze
dressing.
Wounds • Best: Clean wounds by scrubbing gently with gauze and chlorhexidine gluconate solution (if
(Role 1c) available) in clean water, followed by gauze dressing. Repeat daily.
• Monitor vital signs.
• Ensure all interventions noted above are completed by TCCC ASM and CLS personnel.
• Conduct inventory of all resources.
• Document all pertinent information on PCC Flowsheet (attached).
• Additional interventions include:
Airway Minimum: Allow casualty to maintain airway.
(Roles 1a/1b/1c) Better: Facial burns may be associated with inhalation injury. Aggressively monitor airway
status and consider early surgical airway for respiratory distress or oxygen saturation and/or
EtCO (purple-gold colorimetric device).
2
Best: Given a trauma casualty who is unresponsive or has an airway obstruction, consider early
surgical airway.
Fluid Resuscitation • Minimum: Oral intake of water. Rectal infusion of up to 500mL/h can be supplemented with
(Roles 1a/1b/1c) oral hydration. Better: Oral intake of electrolyte solution.
• Best: Start intravenous (IV) or intraosseous (IO) administration immediately.
NOTE: an IV/IO can be placed through burned skin if necessary.
• Use isotonic crystalloids (i.e., Lactated Ringers).
• DO NOT circumferentially tape lines around extremities; this may further impede circulation
and cause limb ischemia as extremities swell during resuscitation.
• NO bolus (unless hypotensive, in which case, bolus only until palpable pulses are restored).
• Initial IV rate 500mL/h; start while completing initial assessment
• Give fluids per TCCC burn treatment guidelines.
• If resuscitation is delayed, DO NOT try to “catch up” by giving extra fluids.
• Blood products may be used in major burn resuscitation due to coagulopathy, anemia, and
bleeding from escharotomy sites or other traumatic injuries.
• Maintain a UOP of 30–50mL/hr. in adults; decrease or increase isotonic fluid rate by 20–
25% per hour.
• If UOP > 50 mL/hr., then decrease the fluid rate by 20–25% for the next hour and reassess.
• Minimize fluid administration while maintaining organ perfusion; hour- to-hour fluid
management is critical.
• 8–12 hr post-burn, if the hourly IV fluid rate exceeds 1500mL/hr. or if the projected 24-hour
total fluid volume approaches 250 mL/kg consult burn team or medical director.
• 24–48 hr post burn, plasma is lost into the burned and unburned tissues, causing
hypovolemic shock (when burn size is >20%). The goal of burn-shock resuscitation is to
replace these ongoing losses while avoiding over-resuscitation.
• 48–72 hr post-burn, completion of the resuscitation is marked by stabilizing hemodynamic
parameters and reduction of IV fluid rate to a maintenance level.
Hypothermia • Hypothermia prevention is extremely important for burn patients.
(Roles 1a/1b/1c) • For Burns >20%, place the casualty in the Heat-Reflective Shell or Blizzard Survival
blanket for the Hypothermia Prevention Kit to both cover the burned areas and prevent
hypothermia.
• Use Blood/Fluid Warmer as needed and if available.
Pain Control Analgesia in accordance with the PCC Guidelines may be administered to treat burn pain.
(Roles 1a/1b/1c)
(continues)
36 | JSOM Volume 22, Edition 1 / Sping 2022