Page 115 - 2022 Spring JSOM
P. 115
FIGURE 2 PT/aPTT/fibrinogen measurements at dilutions of whole blood (WB) with canine FDP reconstituted with sterile water, an HBOC,
canine FDP reconstituted at HBOC, and an equal volume dilution with a 1:1 HBOC and FDP reconstituted with water.
*p < .05 versus whole blood, p < .05 versus same % FDP-only.
δ
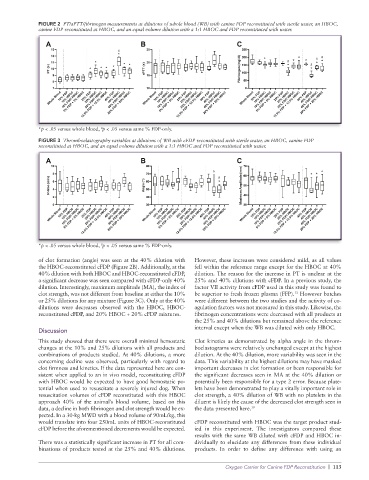
FIGURE 3 Thromboelastography variables at dilutions of WB with cFDP reconstituted with sterile water, an HBOC, canine FDP
reconstituted at HBOC, and an equal volume dilution with a 1:1 HBOC and FDP reconstituted with water.
*p < .05 versus whole blood, p < .05 versus same % FDP-only.
δ
of clot formation (angle) was seen at the 40% dilution with However, these increases were considered mild, as all values
the HBOC-reconstituted cFDP (Figure 2B). Additionally, at the fell within the reference range except for the HBOC at 40%
40% dilution with both HBOC and HBOC-reconstituted cFDP, dilution. The reason for the increase in PT is unclear at the
a significant decrease was seen compared with cFDP-only 40% 25% and 40% dilutions with cFDP. In a previous study, the
dilution. Interestingly, maximum amplitude (MA), the index of factor VII activity from cFDP used in this study was found to
13
clot strength, was not different from baseline at either the 10% be superior to fresh frozen plasma (FFP). However batches
or 25% dilutions for any mixture (Figure 3C). Only at the 40% were different between the two studies and the activity of co-
dilutions were decreases observed with the HBOC, HBOC- agulation factors was not measured in this study. Likewise, the
reconstituted cFDP, and 20% HBOC + 20% cFDP mixtures. fibrinogen concentrations were decreased with all products at
the 25% and 40% dilutions but remained above the reference
interval except when the WB was diluted with only HBOC.
Discussion
This study showed that there were overall minimal hemostatic Clot kinetics as demonstrated by alpha angle in the throm-
changes at the 10% and 25% dilutions with all products and boelastograms were relatively unchanged except at the highest
combinations of products studied. At 40% dilutions, a more dilution. At the 40% dilution, more variability was seen in the
concerning decline was observed, particularly with regard to data. This variability at the highest dilutions may have masked
clot firmness and kinetics. If the data represented here are con- important decreases in clot formation or been responsible for
sistent when applied to an in vivo model, reconstituting cFDP the significant decreases seen in MA at the 40% dilution or
with HBOC would be expected to have good hemostatic po- potentially been responsible for a type 2 error. Because plate-
tential when used to resuscitate a severely injured dog. When lets have been demonstrated to play a vitally important role in
resuscitation volumes of cFDP reconstituted with this HBOC clot strength, a 40% dilution of WB with no platelets in the
approach 40% of the animal’s blood volume, based on this diluent is likely the cause of the decreased clot strength seen in
data, a decline in both fibrinogen and clot strength would be ex- the data presented here. 19
pected. In a 30-kg MWD with a blood volume of 90mL/kg, this
would translate into four 250mL units of HBOC-reconstituted cFDP reconstituted with HBOC was the target product stud-
cFDP before the aforementioned decrements would be expected. ied in this experiment. The investigators compared these
results with the same WB diluted with cFDP and HBOC in-
There was a statistically significant increase in PT for all com- dividually to elucidate any differences from these individual
binations of products tested at the 25% and 40% dilutions. products. In order to define any difference with using an
Oxygen Carrier for Canine FDP Reconstitution | 113