Page 95 - 2020 JSOM Winter
P. 95
Each satellite population had the equivalent of a Role 1 med- time of the local outbreak. This deficiency led to the reliance
5
ical team (aid station with an advance practice medic or cre- on the combat casualty movement system. Within the com-
dentialed clinician), and the main population initially had a bat casualty movement paradigm, patients in austere locations
six-person Role 2 asset (medical/surgical stabilization team). are normally evacuated to higher levels of care to reduce the
An evacuation plan, modified from trauma managements burden upon the small forward medical teams. An infectious
plans, was developed to determine when an evacuation to the disease, especially one easily transmitted by respiratory drop-
main population was to occur; this was predicated on the need lets, challenged the wisdom of following this practice. With
for supplementary oxygen. If patients became hypoxic, as evi- COVID-19, the youthful demographic within the military has
denced by pulse oximetry readings of less than 92% on room a relatively low risk of requiring intensive care and a low death
air, they would need to be evacuated to the higher level of care. rate. Even if the disease were deadlier, considering the health
6
Vital signs were collected twice a day and tracked and moni- of the overall population is an important part of medicine.
tored by the next highest level of care. All locations instituted
social distancing, disinfection protocols, screening, and quar- This case series highlights the effectiveness of isolating con-
antine/isolation procedures during the period to help prevent taminated constituent populations of a greater population in
spread of potential infections. 4 an isolated and austere environment. There were concerns
with this approach given most early reports were in locations
with easy access to a hospital, with care policies with a low
Results
threshold for admission along with resources to quickly man-
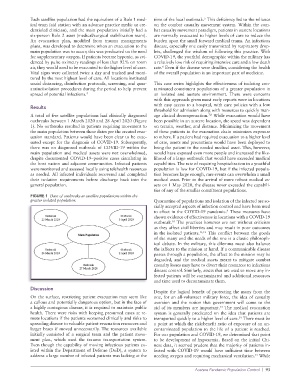
A total of five satellite populations had clinically diagnosed age clinical decompensation. While evacuation would have
7,8
outbreaks between 1 March 2020 and 28 April 2020 (Figure been possible in an austere location, the speed was dependent
1). No outbreaks resulted in patients requiring movement to on terrain, weather, and distance. Minimizing the movement
the main population between these dates per the created evac- of these patients in the evacuation chain minimizes exposure
uation standard. Patients would have been clear to be evac- to others. If a patient had required evacuation to a higher level
uated except for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Subsequently, of care, assets and precautions would have been deployed to
there was no diagnosed outbreak of COVID-19 within the bring the patient to the needed medical asset. This, however,
main population and medical assets were not overwhelmed, would have exposed even more people and increased the like-
despite documented COVID-19–positive cases circulating in lihood of a large outbreak that would have exceeded medical
the host nation and adjacent communities. Infected patients capabilities. The rate of requiring hospitalization in a youthful
were monitored and assessed locally using telehealth resources population is low for COVID-19, but if the infected popula-
as needed. All infected individuals recovered and completed tion becomes large enough, rare events can overwhelm a small
their isolation requirements before discharge back into the medical asset. Prior to the arrival of more robust medical as-
general population. sets on 1 May 2020, the disease never exceeded the capabili-
ties of any of the smaller constituent populations.
FIGURE 1 Date of outbreaks at satellite populations within the
greater isolated population. Quarantine of populations and isolation of the infected are so-
cially accepted aspects of infection control and have been used
to effect in the COVID-19 pandemic. These measures have
9
shown evidence of effectiveness in locations with a COVID-19
outbreak. The practices however are not without criticism
10
as they affect civil liberties and may result in poor outcomes
in the isolated patients. 11,12 This conflict between the goods
of the many and the needs of the one is a classic philosoph-
ical debate. In the military, this dilemma must also balance
the iaffects to the mission at hand. If a communicable disease
passes through a population, the affect to the mission may be
degraded, and the medical assets meant to mitigate combat
casualty losses may have to divert their resources to infectious
disease control. Similarly, assets that are used to move any in-
fected patients will be contaminated and additional resources
and time used to decontaminate them.
Discussion
Despite the logical benefit of protecting the many from the
On the surface, restricting patient evacuation may seem like one, for an all-volunteer military force, the idea of casualty
a callous and potentially dangerous option, but in the face of aversion and the notion that government will come to the
a highly contagious disease, it is required to maintain public aid of its members are important. The medical evacuation
13
health. There were risks with keeping presumed cases at re- system is generally predicated on the idea that patients are
mote locations if the patients worsened clinically and risks to transported quickly to a higher level of care. There must be
14
spreading disease to valuable patient evacuation resources and a point at which the risk:benefit ratio of exposure of an un-
larger bases if moved unnecessarily. The resources available contaminated population to the life of a patient is reached.
initially consisted of a surgical team and the patient move- For our population and COVID-19, we determined that point
ment plan, which used the trauma transportation system. to be development of hypoxemia. Based on the initial Chi-
Even though the capability of moving infectious patients ex- nese data, it seemed prudent that the majority of patients in-
isted within the Department of Defense (DoD), a system to fected with COVID-19 would have sufficient time between
address a large number of infected patients was lacking at the needing oxygen and requiring mechanical ventilation. While
15
Austere Pandemic Population Control | 93