Page 71 - 2020 JSOM Winter
P. 71
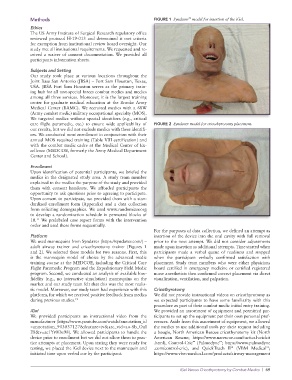
Methods FIGURE 1 Syndaver model for insertion of the iGel.
™
Ethics
The US Army Institute of Surgical Research regulatory office
reviewed protocol H-19-013 and determined it met criteria
for exemption from institutional review board oversight. Our
study met all institutional requirements. We requested and re-
ceived a waiver of consent documentation. We provided all
participants information sheets.
Subjects and Setting
Our study took place at various locations throughout the
Joint Base San Antonio (JBSA) – Fort Sam Houston, Texas,
USA. JBSA Fort Sam Houston serves as the primary train-
ing hub for all non-special forces combat medics and medics
among all three services. Moreover, it is the largest training
center for graduate medical education at the Brooke Army
Medical Center (BAMC). We recruited medics with a 68W
(Army combat medic) military occupational specialty (MOS).
We targeted medics without special identifiers (e.g., critical
care flight paramedic, etc.) to ensure wide applicability of FIGURE 2 Syndaver model for cricothyrotomy placement.
our results, but we did not exclude medics with these identifi-
ers. We conducted most enrollment in conjunction with their
annual MOS required training (Table VIII certification) and
with the combat medic cadre at the Medical Center of Ex-
cellence (MEDCOE, formerly the Army Medical Department
Center and School).
Enrollment
Upon identification of potential participants, we briefed the
medics in the designated study area. A study team member
explained to the medics the purpose of the study and provided
them with consent handouts. We afforded participants the
opportunity to ask questions prior to agreeing to participate.
Upon consent to participate, we provided them with a stan-
dardized enrollment form (Appendix) and a data collection
form soliciting demographics. We used www.randomizer.org
to develop a randomization schedule in permuted blocks of
11
10. We prelabeled case report forms with the intervention
order and used these forms sequentially.
For the purposes of data collection, we defined an attempt as
Platform insertion of the device into the oral cavity with full removal
We used mannequins from Syndaver (https://syndaver.com/) – prior to the next attempt. We did not consider adjustments
adult airway trainer and cricothyrotomy trainer (Figures 1 made upon insertion as additional attempts. Time started when
and 2). We selected these models for two reasons. First, this participants made a verbal queue of readiness and stopped
is the mannequin model of choice by the advanced medic when the participant verbally confirmed satisfaction with
training course at the MEDCOE, including the Critical Care placement. Study team members who were either physicians
Flight Paramedic Program and the Expeditionary Field Medic board certified in emergency medicine or certified registered
program. Second, we conducted an analysis of available low- nurse anesthetists then confirmed correct placement via direct
fidelity (e.g., no interactive simulation) mannequins on the visualization, ventilation, and palpation.
market and our study team felt that this was the most realis-
tic model. Moreover, our study team had experience with this Cricothyrotomy
platform, for which we received positive feedback from medics We did not provide instructional videos on cricothyrotomy as
during previous studies. 12 we expected participants to have some familiarity with this
procedure as part of their combat medic initial entry training.
iGel We provided an assortment of equipment and permitted par-
We provided participants an instructional video from the ticipants to set up the equipment per their own personal pref-
manufacturer (https://www.youtube.com/watch?annotation_id erences. Aside from this assortment of equipment, we allowed
=annotation_903037127&feature=iv&src_vid=ao-Sb_Oul the medics to use additional tools per their request including
E8&v=ae1Yr0fbz98). We allowed participants to handle the a bougie, North American Rescue cricothyrotomy kit (North
device prior to enrollment but we did not allow them to prac- American Rescue; https://www.narescue.com/tactical-crickit
™
™
tice attempts at placement. Upon stating they were ready for .html), Control-Cric (Pulmodyne ; https://www.pulmodyne
™
™
testing, we placed the iGel device next to the mannequin and .com/control-cric), and QuickTrach II (VBM Medical ;
initiated time upon verbal cue by the participant. https://www.vbm-medical.com/products/airway-management
iGel Versus Cricothyrotomy by Combat Medics | 69