Page 148 - JSOM Fall 2020
P. 148
APPENDIX A: AIRWAY EQUIPMENT
AIRWAY EQUIPMENT and respiratory acidosis. Recommended order: endotracheal
• Minimum (ruck/aid bag): Nasopharyngeal airway, cri- tube-capnograph-HME device (proximal to distal)
cothyrotomy kit; BVM with PEEP valve
• Better: Minimum PLUS supraglottic airway, gum elastic NASOGASTRIC/OROGASTRIC TUBE
bougie to facilitate intubation, nasogastric/orogastric tube Placement of a nasogastric (NG) or orogastric (OG) tube
• Best: Better PLUS endotracheal tubes, direct laryngos- should be considered following intubation of a patient in or-
copy, or video laryngoscopy equipment der to decompress gastric contents, prevent aspiration and
gastric distention.
WAVEFORM CAPNOGRAPHY • If only supraglottic airway access is available, consider
• Minimum: Colorimetric ETCO detector using a supraglottic device that incorporates an orogas-
2
• Better: Portable capnometer tric tube port.
• Best: Waveform capnography on patient monitor • Always measure the distance from nose to stomach and
note the distance prior to insertion, then verify epigas-
See Appendix G for Capnography Interpretation.
tric sounds. Verify placement with second practitioner if
sounds are questionable or difficult to auscultate.
HEAT-MOISTURE EXCHANGER • Do not feed, aggressively hydrate or give oral medications
Heat-moisture exchangers (HME) are small, relatively inex- through an OGT or NGT without telemedicine guidance.
pensive, in-line ETT adjuncts that contain hygroscopic salts Always reassess tube position prior to putting anything
that use differences in vapor pressure, expired moisture con- into stomach to ensure proper gastric placement. Feeding
tent, and the patient’s temperature to increase the humidity should not be considered until 72 hours after injury in the
of inspired air. Increased moisture on inspiration helps main- PFC environment. If volume instilled is too large or rate is
tain alveolar moisture. Capnography should not be positioned too fast, there is increased risk for vomiting. If feeding or
in-line following HME as these moisture devices can increase hydration is begun through an OGT or NGT, they must
breathing resistance and work of respiration, as well as in- be accurate, measured, and monitored. Safe airway man-
crease breathing apparatus dead space (especially in pediatric agement takes precedence over nutrition.
patients). This may lead to potential worsening hypercapnia
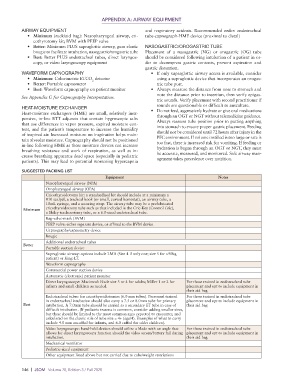
SUGGESTED PACKING LIST
Equipment Notes
Nasopharyngeal airway (NPA)
Oropharyngeal airway (OPA)
Cricothyroidotomy kit: a standardized kit should include at a minimum a
#10 scalpel, a tracheal hook (or small, curved hemostat), an airway tube, a
10mL syringe, and a securing strap. The airway tube may be a prefabricated
Minimum cricothyroidotomy tube such as that included in the Cric-Key (Control Cric),
a Shiley tracheostomy tube, or a 6.0-sized endotracheal tube.
Bag-valve-mask (BVM)
PEEP valve: either separate device, or affixed to the BVM device
Capnography/capnometry device
Bougie
Additional endotracheal tubes
Better
Portable suction device
Supraglottic airway: options include LMA (Size 4 if only one; size 5 for >90kg
patient) or King-LT.
Waveform capnography
Commercial power suction device
Automatic (electronic) patient monitor
Direct laryngoscope: Macintosh blade size 3 or 4 for adults; Miller 1 or 2 for For those trained in endotracheal tube
infants and small children as needed. placement and opt to include equipment in
their aid bag
Endotracheal tubes: for cricothyroidotomies (6.0 mm tubes). Personnel trained For those trained in endotracheal tube
in endotracheal intubation should also carry a 7.5 or 8.0mm tube for primary placement and opt to include equipment in
Best intubation. A 7.0mm tube should be carried as a secondary ET tube in case of their aid bag
difficult intubation. (If pediatric trauma is common, consider adding smaller sizes,
but these should be limited to the most common ages expected to encounter, and
calculated on the classic rule of tube size = 4+ (age/4). Examples of what to carry
include 4.0 mm uncuffed for infants, and 6.0 cuffed for older children).
Video laryngoscope: hand-held devices should utilize a blade with an angle that For those trained in endotracheal tube
allows for direct laryngoscopy function should the video screen/battery fail during placement and opt to include equipment in
intubation. their aid bag
Mechanical ventilator
Pediatric-sized equipment
Other equipment listed above but not carried due to cube/weight restrictions
146 | JSOM Volume 20, Edition 3 / Fall 2020