Page 106 - JSOM Fall 2019
P. 106
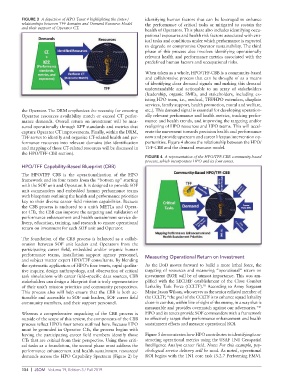
FIGURE 3 A depiction of HPO Tenet 4 highlighting the (inter-) identifying human factors that can be leveraged to enhance
relationships between TFF domains and Demand Resource Model the performance of critical tasks or mitigated to sustain the
and their support of Operator CT.
health of Operators. This phase also includes identifying occu-
pational exposures and health risk factors associated with crit-
ical tasks and conditions under which performance is expected
to degrade or compromise Operator sustainability. The third
phase of this process also involves identifying operationally
relevant health and performance metrics associated with the
predefined human factors and occupational risks.
When taken as a whole, HPO/TFF-CBB is a community-based
and collaborative process that can be thought of as a means
of identifying clear demand signals and making this demand
understandable and actionable to an array of stakeholders
(leadership, organic SMEs, and stakeholders, including ex-
isting HPO team, i.e., medical, TFF/HPO extenders, chaplain
services, family support, health promotion, moral and welfare,
the Operator. The DRM emphasizes the necessity for ensuring etc.). This demand signal is essential for developing operation-
Operator resources availability match or exceed CT perfor- ally relevant performance and health metrics, tracking perfor-
mance demands. Overall return on investment will be mea- mance and health trends, and improving the targeting and/or
sured operationally through KPP standards and metrics that realigning of HPO resources and HPO teams. This will accel-
capture Operator CT improvements. Finally, within the DRM, erate the movement towards precision health and performance
TFF serves to identify and organize CT-related health and per- now and provide upstream and career lifespan intervention op-
formance resources into relevant domains (the identification portunities. Figure 4 shows the relationship between the HPO/
and mapping of these CT-related resources will be discussed in TFF-CBB and the demand resource model.
the HPO/TFF-CBB section).
FIGURE 4 A representation of the HPO/TFF-CBB community-based
process, which incorporates HPO and its four tenets.
HPO/TFF Capability-Based Blueprint (CBB)
The HPO/TFF CBB is the operationalization of the HPO
framework and its four tenets from the “bottom up” starting
with the SOF unit and Operator. It is designed to provide SOF
unit commanders and embedded human performance teams
with blueprints outlining the health and performance priorities
key to their diverse career field mission capabilities. Because
the CBB process is anchored to a unit’s METLs and Opera-
tor CTs, the CBB can improve the targeting and validation of
performance enhancement and health sustainment service de-
livery, education, training, and research to ensure operational
return on investment for each SOF unit and Operator.
The foundation of the CBB process is balanced as a collab-
oration between SOF unit leaders and Operators from the
participating career field, embedded and/or organic human
performance teams, installation support agency personnel, Measuring Operational Return on Investment
and subject matter expert HPO/TFF consultants. By blending
the systematic application of HPO’s four tenets, rapid qualita- As the DoD moves forward to build a more lethal force, the
tive inquiry, design anthropology, and observation of critical targeting of resources and measuring “operational” return on
task simulations with career field–specific data sources, CBB investment (ROI) will be of utmost importance. This was am-
stakeholders can design a blueprint that is truly representative plified with the SECDEF establishment of the Close Combat
of their unit’s mission priorities and community perspectives. Lethality Task Force (CCLTF). According to Army Sergeant
20
This process also will help ensure that the CBB is both ac- Major Jason Wilson, who serves as the senior enlisted member of
tionable and accessible to SOF unit leaders, SOF career field the CCLTF, “the goal of the CCLTF is to enhance squad lethality
community members, and their support personnel. close-in combat, within line of sight of the enemy, in a way that is
measurable and provides overmatch against our adversaries.”
21
Whereas a comprehensive unpacking of the CBB process is HPO and its tenets provide SOF commanders with a framework
outside of the scope of this review, the components of the CBB to effectively target their performance enhancement and health
process reflect HPO’s four tenets outlined here. Because HPO sustainment efforts and measure operational ROI.
must be grounded in Operator CTs, the process begins with
having the participating career field members identify those Figure 5 demonstrates how HPO contributes to identifying/con-
CTs that are critical from their perspective. Using these criti- structing operational metrics using the USAF 1N1 Geospatial
cal tasks as a foundation, the second phase must address the Intelligence Analyst career field. Note: For this example, psy-
performance enhancement and health sustainment resources/ chological service delivery will be used. As noted, operational
demands across the HPO Capability Spectrum (Figure 2) by ROI begins with the 1N1 core task (3.2.7 Performing FMV).
104 | JSOM Volume 19, Edition 3 / Fall 2019