Page 85 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Fall 2016
P. 85
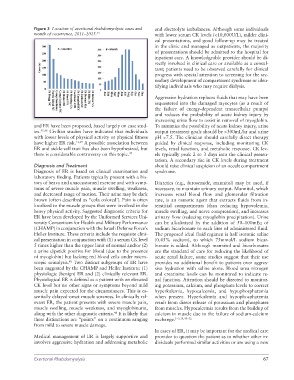
Figure 3 Location of exertional rhabdomyolysis cases and and electrolyte imbalances. Although some individuals
month of occurrence, 2011–2015. 35 with lower serum CK levels (<10,000U/L), milder clini-
cal presentations, and good follow-up may be treated
in the clinic and managed as outpatients, the majority
of presentations should be admitted to the hospital for
inpatient care. A knowledgeable provider should be di-
rectly involved in clinical care or available as a consul-
tant; patients need to be observed carefully for clinical
progress with special attention to screening for the sec-
ondary development of compartment syndrome or iden-
tifying individuals who may require dialysis.
Aggressive hydration replaces fluids that may have been
sequestered into the damaged myocytes (as a result of
the failure of energy-dependent transcellular pumps)
and reduces the probability of acute kidney injury by
increasing urine flow to assist in removal of myoglobin.
and ER have been proposed, based largely on case stud- To minimize the possibility of acute kidney injury, urine
ies. 45,46 Civilian studies have indicated that individuals output treatment goals should be >300mL/hr and urine
with lower levels of physical activity or physical fitness pH >7.5. The clinician should carefully direct therapy
have higher ER risk. 12,29 A possible association between guided by clinical response, including monitoring CK
ER and sickle-cell trait has also been hypothesized, but levels, renal function, and metabolic response. CK lev-
there is considerable controversy on this topic. 47 els typically peak 2 to 3 days into the clinical presen-
tation. A secondary rise in CK levels during treatment
Diagnosis and Treatment should raise clinical suspicion of an occult compartment
Diagnosis of ER is based on clinical examination and syndrome.
laboratory finding. Patients typically present with a his-
tory of heavy and unaccustomed exercise and with symp- Diuretics (e.g., furosemide, mannitol) may be used, if
toms of severe muscle pain, muscle swelling, weakness, necessary, to maintain urinary output. Mannitol, which
and decreased range of motion. Their urine may be dark increases renal blood flow and glomerular filtration
brown (often described as “cola colored’). Pain is often rate, is an osmotic agent that extracts fluids from in-
localized to the muscle groups that were involved in the terstitial compartments (thus reducing hypovolemia,
heavy physical activity. Suggested diagnostic criteria for muscle swelling, and nerve compression), and increases
ER have been developed by the Uniformed Services Uni- urinary flow (reducing myoglobin precipitation). Urine
versity Consortium for Health and Military Performance can be alkalinized by the addition of 50–100mEq of
(CHAMP) in conjunction with the Israeli Defense Force’s sodium bicarbonate to each liter of administered fluid.
Heller Institute. These criteria include the requisite clini- The proposed ideal fluid regimen is half isotonic saline
cal presentation in conjunction with (1) a serum CK level (0.45% sodium), to which 75mmol/L sodium bicar-
5 times higher than the upper limit of normal and/or (2) bonate is added. Although mannitol and bicarbonates
a urine dipstick positive for blood (due to the presence are the standard of care for reducing the likelihood of
of myoglobin) but lacking red blood cells under micro- acute renal failure, some studies suggest that their use
scopic urinalysis. Two distinct subgroups of ER have provides no additional benefit to patients over aggres-
48
been suggested by the CHAMP and Heller Institute: (1) sive hydration with saline alone. Blood urea nitrogen
physiologic (benign) ER and (2) clinically relevant ER. and creatinine levels can be monitored to indicate re-
Physiological ER is defined as a patient with an elevated nal function. Attention should be directed to monitor-
CK level but no other signs or symptoms beyond mild ing potassium, calcium, and phosphate levels to correct
muscle pain expected for the circumstances. This is es- hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypophosphatemia
sentially delayed-onset muscle soreness. In clinically rel- when present. Hyperkalemia and hypophosphatemia
evant ER, the patient presents with severe muscle pain, result from direct release of potassium and phosphates
muscle swelling, muscle weakness, and myoglobinuria, from muscles. Hypocalcemia results from the buildup of
along with the other diagnostic criteria. It is likely that calcium in muscle due to the failure of sodium-calcium
48
these distinctions are “points” on a continuum ranging exchange. 1–3,14,49–52
from mild to severe muscle damage.
In cases of ER, it may be important for the medical care
Medical management of ER is largely supportive and provider to question the patient as to whether other in-
involves aggressive hydration and addressing metabolic dividuals performed similar activities or are using a new
Exertional Rhabdomyolysis 67