Page 20 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Fall 2015
P. 20
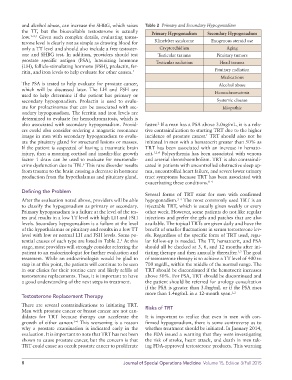
and alcohol abuse, can increase the SHBG, which raises Table 2 Primary and Secondary Hypogonadism
the TT, but the bioavailable testosterone is actually Primary Hypogonadism Secondary Hypogonadism
low. 1–3,5 Given such complex details, evaluating testos-
terone level is clearly not as simple as drawing blood for Klinefelter syndrome Exogenous steroid use
only a TT level and should also include a free testoster- Cryptorchidism Aging
one and SHBG test. In addition, providers should test Testicular trauma Pituitary tumors
prostate specific antigen (PSA), luteinizing hormone Testicular radiation Head trauma
(LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), prolactin, fer-
ritin, and iron levels to help evaluate for other causes. 1 Pituitary radiation
Medications
The PSA is tested to help evaluate for prostate cancer, Alcohol abuse
which will be discussed later. The LH and FSH are Hemochromatosis
used to help determine if the patient has primary or
secondary hypogonadism. Prolactin is used to evalu- Systemic disease
ate for prolactinomas that can be associated with sec- Idiopathic
ondary hypogonadism. The ferritin and iron levels are
determined to evaluate for hemochromatosis, which is
also associated with secondary hypogonadism. Provid- faster. If a man has a PSA above 3.0ng/mL, it is a rela-
2
ers could also consider ordering a magnetic resonance tive contraindication to starting TRT due to the higher
image in men with secondary hypogonadism to evalu- incidence of prostate cancer. TRT should also not be
1
ate the pituitary gland for structural lesions or masses. initiated in men with a hematocrit greater than 50% as
If the patient is suspected of having a traumatic brain TRT has been associated with an increase in hemato-
injury, then a morning cortisol and insulin-like growth crit. 1,2,4 Polycythemia has been associated with venous
factor 1 draw can be used to evaluate for neuroendo- and arterial thromboembolism. TRT is also contraindi-
crine dysfunction due to TBI. This rare disorder results cated in patients with uncontrolled obstructive sleep ap-
6
from trauma to the brain causing a decrease in hormone nea, uncontrolled heart failure, and severe lower urinary
production from the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. tract symptoms because TRT has been associated with
exacerbating these conditions. 1–4
Defining the Problem
Several forms of TRT exist for men with confirmed
After the evaluation noted above, providers will be able hypogonadism. The most commonly used TRT is an
1–4
to classify the hypogonadism as primary or secondary. injectable TRT, which is usually given weekly or every
Primary hypogonadism is a failure at the level of the tes- other week. However, some patients do not like regular
tes and results in a low TT level with high LH and FSH injections and prefer the gels and patches that are also
levels. Secondary hypogonadism is a failure at the level available. The topical TRTs are given daily and have the
of the hypothalamus or pituitary and results in a low TT benefit of smaller fluctuations in serum testosterone lev-
level with low or normal LH and FSH levels. Some po- els. Regardless of the specific form of TRT used, regu-
tential causes of each type are listed in Table 2. At this lar follow-up is needed. The TT, hematocrit, and PSA
1
stage, most providers will strongly consider referring the should all be checked at 3, 6, and 12 months after ini-
patient to an endocrinologist for further evaluation and tiating therapy and then annually thereafter. The goal
1,2
treatment. While an endocrinologist would be glad to of testosterone therapy is to achieve a TT level of 400 to
step in at this point, the patients will continue to be seen 700 mg/dL, within the middle of the normal range. The
in our clinics for their routine care and likely refills of TRT should be discontinued if the hematocrit increases
testosterone replacements. Thus, it is important to have above 50%. For PSA, TRT should be discontinued and
a good understanding of the next steps in treatment. the patient should be referred for urology consultation
if the PSA is greater than 3.0ng/mL or if the PSA rises
more than 1.4ng/mL in a 12-month span. 1,2
Testosterone Replacement Therapy
There are several contraindications to initiating TRT. Risks of TRT
Men with prostate cancer or breast cancer are not can-
didates for TRT because therapy can accelerate the It is important to realize that even in men with con-
growth of either cancer. This worsening is a reason firmed hypogonadism, there is some controversy as to
1–4
why a prostate examination is indicated early in the whether treatment should be initiated. In January 2014,
evaluation. It is important to note that TRT has not been the FDA issued a warning that they were investigating
shown to cause prostate cancer, but the concern is that the risk of stroke, heart attack, and death in men tak-
TRT could cause an occult prostate cancer to proliferate ing FDA-approved testosterone products. This warning
8 Journal of Special Operations Medicine Volume 15, Edition 3/Fall 2015