Page 91 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Summer 2014
P. 91
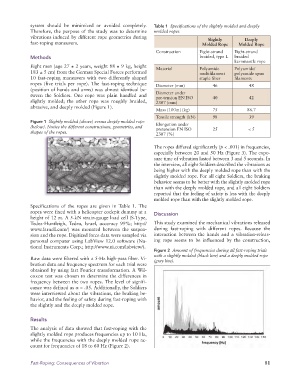
system should be minimized or avoided completely. Table 1 Specifications of the slightly molded and deeply
Therefore, the purpose of the study was to determine molded ropes
vibrations induced by different rope geometries during Slightly Deeply
fast-roping maneuvers. Molded Rope Molded Rope
Construction Eight-strand Eight-strand
Methods braided, type L braided
kernmantle rope
Eight men (age 27 ± 2 years, weight 88 ± 9 kg, height Material Polyamide Polyamide/
183 ± 5 cm) from the German Special Forces performed multifilament polyamide spun
10 fast-roping maneuvers with two differently shaped staple fiber filaments
ropes (five trials per rope). The fast-roping technique Diameter (mm) 46 48
(position of hands and arms) was almost identical be-
tween the Soldiers. One rope was plain handled and Diameter under 40 42
pre-tension EN ISO
slightly molded; the other rope was roughly braided, 2307 (mm)
abrasive, and deeply molded (Figure 1).
Mass (100m) (kg) 75 86.7
Tensile strength (kN) 98 39
Figure 1 Slightly molded (above) versus deeply molded rope
(below). Notice the different constructions, geometries, and Elongation under 25 < 5
pretension EN ISO
shapes of the ropes. 2307 (%)
The ropes differed significantly (p < .001) in frequencies,
especially between 20 and 50 Hz (Figure 3). The expo-
sure time of vibration lasted between 3 and 5 seconds. In
the interview, all eight Soldiers described the vibrations as
being higher with the deeply molded rope than with the
slightly molded rope. For all eight Soldiers, the braking
behavior seems to be better with the slightly molded rope
than with the deeply molded rope, and all eight Soldiers
reported that the feeling of safety is less with the deeply
molded rope than with the slightly molded rope.
Specifications of the ropes are given in Table 1. The
ropes were fixed with a helicopter cockpit dummy at a Discussion
height of 12 m. A 5-kN strain-gauge load cell (S-Type,
Tedea-Huntleigh, Tedea, Israel, accuracy 99%; http:// This study examined the mechanical vibrations released
www.farnell.com/) was mounted between the suspen- during fast-roping with different ropes. Because the
sion and the rope. Digitized force data were sampled via interaction between the hands and a vibration-releas-
personal computer using LabView 12.0 software (Na- ing rope seems to be influenced by the construction,
tional Instruments Corp.; http://www.ni.com/labview/).
Figure 2 Amount of frequencies during all fast-roping trials
with a slightly molded (black line) and a deeply molded rope
Raw data were filtered with a 5-Hz high-pass filter. Vi- (gray line).
bration data and frequency spectrum for each trial were
obtained by using fast Fourier transformation. A Wil-
coxon test was chosen to determine the differences in
frequency between the two ropes. The level of signifi-
cance was defined as α = .05. Additionally, the Soldiers
were interviewed about the vibrations, the braking be-
havior, and the feeling of safety during fast-roping with
the slightly and the deeply molded rope.
Results
The analysis of data showed that fast-roping with the
slightly molded rope produces frequencies up to 10 Hz,
while the frequencies with the deeply molded rope ac-
count for frequencies of 18 to 60 Hz (Figure 2).
Fast-Roping: Consequences of Vibration 81