Page 87 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Summer 2014
P. 87
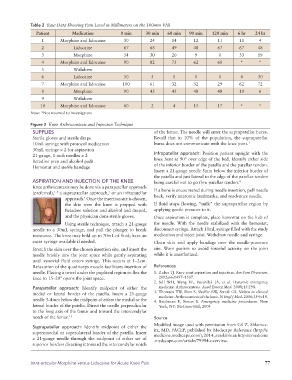
Table 2 Raw Data Showing Pain Level in Millimeters on the 100mm VAS
Patient Medication 0 min 30 min 60 min 90 min 120 min 6 hr 24 hr
1 Morphine and lidocaine 30 24 14 12 11 10 4
2 Lidocaine 67 68 49 48 67 67 48
3 Morphine 54 30 20 9 0 33 19
4 Morphine and lidocaine 90 82 75 62 60 * *
5 Withdrew
6 Lidocaine 50 5 0 0 0 8 30
7 Morphine and lidocaine 100 61 32 32 29 62 72
8 Morphine 90 45 45 48 48 19 6
9 Withdrew
10 Morphine and lidocaine 80 2 4 15 17 * *
Note: *Not returned to investigators
Figure 2 Knee Arthrocentesis and Injection Technique
SUPPLIES of the femur. The needle will enter the suprapatellar bursa.
Sterile gloves and sterile drape Recall that in 10% of the population, the suprapatellar
10mL syringe with protocol medication bursa does not communicate with the knee joint. 1
30mL syringe × 2 for aspiration
21-gauge, 1-inch needles × 2 Infrapatellar approach: Position patient upright with the
Betadine prep and alcohol pads knee bent at 90° over edge of the bed. Identify either side
Hemostat and sterile bandage of the inferior border of the patella and the patellar tendon.
Insert a 21-gauge needle 5mm below the inferior border of
the patella and just lateral to the edge of the patellar tendon
ASPIRATION AND INJECTION OF THE KNEE being careful not to go thru patellar tendon. 4
Knee arthrocentesis may be done via a parapatellar approach If a bone is encountered during needle insertion, pull needle
1
1–3
(preferred), a suprapatellar approach, or an infrapatellar back, verify anatomic landmarks, and readvance needle.
4
approach. Once the insertion site is chosen,
the skin over the knee is prepped with If fluid stops flowing, “milk” the suprapatellar region by
Betadine solution and alcohol and draped, applying gentle pressure to it.
and the physician dons sterile gloves. Once aspiration is complete, place hemostat on the hub of
Using sterile technique, attach a 21-gauge the needle. With the needle stabilized with the hemostat,
needle to a 30mL syringe, and pull the plunger to break disconnect syringe. Attach 10mL syringe filled with the study
resistance. The knee may hold up to 70mL of fluid; have an medication and inject joint. Withdraw needle and syringe.
extra syringe available if needed. Clean skin and apply bandage over the needle-puncture
Stretch the skin over the chosen insertion site, and insert the site. Warn patient to avoid forceful activity on the joint
needle briskly into the joint space while gently aspirating while it is anesthetized.
until synovial fluid enters syringe. This occurs at 1–2cm.
Relaxation of the quadriceps muscle facilitates insertion of References
needle. Placing a towel under the popliteal region to flex the 1. Zuber TJ. Knee joint aspiration and injection. Am Fam Physician.
knee to 15–20° opens the joint space. 2002;66:1497–1507.
2. Self WH, Wang EE, Vozenilek JA, et al. Dynamic emergency
Parapatellar approach: Identify midpoint of either the medicine. Arthrocentesis. Acad Emerg Med. 2008;15:298.
medial or lateral border of the patella. Insert a 21-gauge 3. Thomsen TW, Shen S, Shaffer RW, Setnik GS. Videos in clinical
medicine. Arthrocentesis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:e19.
needle 3–4mm below the midpoint of either the medial or the 4. Reichman E, Simon B. Emergency medicine procedures. New
lateral border of the patella. Direct the needle perpendicular York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2004
to the long axis of the femur and toward the intercondylar
notch of the femur. 1-3 Source
Modified image used with permission from Gil Z. Shlamov-
Suprapatellar approach: Identify midpoint of either the itz, MD, FACEP, published by Medscape Reference (http://e
superomedial or superolateral border of the patella. Insert medicine.medscape.com/), 2014, available at: http://emedicine
a 21-gauge needle through the midpoint of either set of .medscape.com/article/79994-overview.
superior borders directing it toward the intercondylar notch
Intra-articular Morphine versus Lidocaine for Acute Knee Pain 77