Page 44 - JSOM Fall 2025
P. 44
system (La classification Clinique des Maladies du SMUR), antiplatelet agents (AAP) or anticoagulants (AC) (15; 8.6%).
3
which ranks severity from 1 (stable patients requiring no med- No transfusion of lyophilized plasma was performed.
ical treatment) to 6 (patient deceased prior to medical team
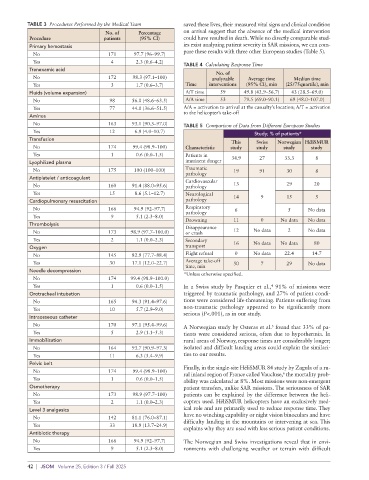
arrival). In this study, patients classified as CCMS 4 or 5 (pre- FIGURE 1 Flow chart of the study.
senting a functional or vital prognosis, with or without the
need for resuscitation) were also considered to be in imminent Total no. of patients
danger. causing a SAR trigger
n=215
Secondary Endpoints
In addition to the primary endpoint, three quantitative second-
ary endpoints were examined.
Patients whose SAR
1. Reason for mission activation, categorized as: was cancelled
• Diving accident n=36
• Plane crash
• Cardiac distress
• Neurological distress
Missing patients not
• Respiratory distress found by the SAR team
• Disappearance n=4
• Gynecology
• Infection
• Drowning
• Patient transport Total number of patients
• Trauma whose data were analyzed
• Digestive emergencies n=175
2. Procedures performed by the medical team during the
mission.
3. Speed of the medical response. Number of patients in Number of patients
“imminent danger” at the not considered to be in
Statistical Analysis arrival of the SAR “imminent danger” at the
After data extraction from the mission report forms, all in- n=61 time of treatment
formation was anonymized. Categorical data are expressed as n=114
percentages with corresponding 95% CIs.
SAR = search and rescue.
Results
TABLE 2 Reasons for Departure
Data were available for 175 of the 215 patient records (Figure No. of patients
1). Among these, we could not determine whether the patient by reason; Percentage
was in imminent danger for 21 patients (12.0%) due to insuf- Reason for departure n=175 (95% CI)
ficient data. Of these 175 patients, 61 (34.9%; 95% CI 27.4– Diving accident 2 1.1 (0.0–8.1)
42.7) were considered to be in imminent danger (Table 1). Plane crash 11 6.3 (0.0–13.3)
Cardiac distress 22 12.6 (6.3–19.6)
TABLE 1 Number of Patients in Imminent Danger Neurological distress 25 14.3 (8.0–21.3)
No. of patients; Percentage Respiratory distress 10 5.7 (0.0–12.7)
Status n=175 (95% CI)
Disappearance 11 6.3 (0.0–13.3)
Imminent danger 61 34.9 (27.4–42.7) Gynecology 2 1.1 (0.0–8.1)
No imminent danger 93 53.1 (45.7–61.0) Unknown 4 2.3 (0.0–9.3)
Unknown 21 12.0 (4.6–19.8) Infection 3 1.7 (0.0–8.7)
Drowning 19 10.9 (4.6–17.8)
Reasons for launching a mission (Table 2) included traumatic Secondary transport 28 16.0 (9.7–23.0)
pathology (33; 18.9%), patient transfers (28; 16%), neuro- Trauma 33 18.9 (12.6–25.8)
logical distress (25; 14.3%), and cardiac distress (22; 12.6%). Digestive emergency 5 2.9 (0.0–9.8)
Other causes included drownings (19; 10.9%), crashes or lost
individuals (11 each; 6.3% each), respiratory distress (n=10; The average time from mission activation to the helicopter’s
5.7%), digestive emergencies (5; 2.9%), diving accidents and take-off (A/T time) was 49.8 (42.9–56.7) minutes. The average
gynecological emergencies (n=2 each; 1.1% each), and infec- time from activation to arrival at the casualty’s location (A/A
tious emergencies (3; 1.7%). Lost individuals only included time) was 79.5 (69.0–90.1) minutes (Table 4).
individuals who had disappeared and were recovered by the
SAR team with a completed mission report.
Discussion
Procedures performed by the medical team (Table 3) included Primary Endpoint
volume replenishment (77; 44%), oxygen therapy (30; 17.1%), Of the 175 patients, 61 (34.9%) were considered to be in im-
morphine administration (33; 18.9%), and treatment with minent danger. While we cannot confirm that SAR intervention
Search and Rescue Missions Conducted by the French Army | 41