Page 42 - JSOM Fall 2024
P. 42
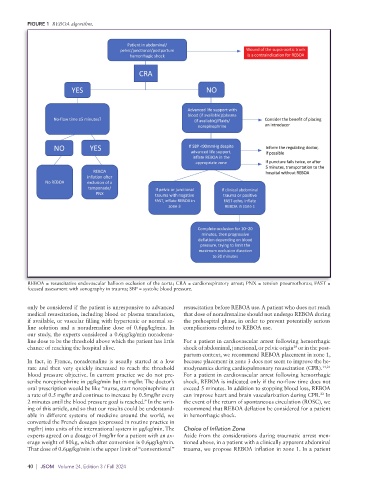
FIGURE 1 REBOA algorithm.
REBOA = resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta; CRA = cardiorespiratory arrest; PNX = tension pneumothorax; FAST =
focused assessment with sonography in trauma; SBP = systolic blood pressure.
only be considered if the patient is unresponsive to advanced resuscitation before REBOA use. A patient who does not reach
medical resuscitation, including blood or plasma transfusion, that dose of noradrenaline should not undergo REBOA during
if available, or vascular filling with hypertonic or normal sa- the prehospital phase, in order to prevent potentially serious
line solution and a noradrenaline dose of 0.6µg/kg/min. In complications related to REBOA use.
our study, the experts considered a 0.6µg/kg/min noradrena-
line dose to be the threshold above which the patient has little For a patient in cardiovascular arrest following hemorrhagic
20
chance of reaching the hospital alive. shock of abdominal, junctional, or pelvic origin or in the post-
partum context, we recommend REBOA placement in zone 1,
In fact, in France, noradrenaline is usually started at a low because placement in zone 3 does not seem to improve the he-
rate and then very quickly increased to reach the threshold modynamics during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). 14,21
blood pressure objective. In current practice we do not pre- For a patient in cardiovascular arrest following hemorrhagic
scribe norepinephrine in µg/kg/min but in mg/hr. The doctor’s shock, REBOA is indicated only if the no-flow time does not
oral prescription would be like “nurse, start norepinephrine at exceed 5 minutes. In addition to stopping blood loss, REBOA
22
a rate of 0.5 mg/hr and continue to increase by 0.5mg/hr every can improve heart and brain vascularization during CPR. In
2 minutes until the blood pressure goal is reached.” In the writ- the event of the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), we
ing of this article, and so that our results could be understand- recommend that REBOA deflation be considered for a patient
able in different systems of medicine around the world, we in hemorrhagic shock.
converted the French dosages (expressed in routine practice in
mg/hr) into units of the international system in µg/kg/min. The Choice of Inflation Zone
experts agreed on a dosage of 3mg/hr for a patient with an av- Aside from the considerations during traumatic arrest men-
erage weight of 80kg, which after conversion is 0.6µg/kg/min. tioned above, in a patient with a clinically apparent abdominal
That dose of 0.6µg/kg/min is the upper limit of “conventional” trauma, we propose REBOA inflation in zone 1. In a patient
40 | JSOM Volume 24, Edition 3 / Fall 2024