Page 90 - JSOM Summer 2024
P. 90
TABLE 1 Technical Specification Comparison Between the CH-47 24 litters would be less functional for the provision of care,
Chinook and UH-60M Blackhawk 17,32 but decreasing it to eight would still exceed the UH-60M’s
UH-60M capacity. Beyond equipment, the CH-47 could carry a larger
Specifications CH-47 Chinook Blackhawk aeromedical team optimized for either mission set—far-
Fuselage length 30 ft, 9 in 12 ft forward DCR/DCS interventions in pre-hospital environments
Fuselage width 7 ft, 6 in 7 ft or rotary-wing critical care air transport.
Fuselage height 6 ft, 5 in 4 ft, 6 in
Fuel capacity 1034 gal 360 gal CH-47 Limitations
Cruise speed 120–140 kts 110–130 kts Although the CH-47 has advantages over the UH-60M, several
Mission range 310nm 275nm limitations exist. First, it is resource-intensive to sustain normal
Max gross weight 50,000 lbs 22,000 lbs CH-47 operations, including more fuel and maintenance per
Litter capacity 24 4 flight hour. The CH-47 also has a larger radar cross section and
Non-crew fully equipped is susceptible to being targeted by advanced enemy radar and
troop seating capacity 33 11 missile systems in flight. CH-47 aircrews also require a slightly
FY2020 cost requests $357.9 million $1,673.4 million larger landing area than the UH-60M because of the inher-
ent size differences between airframes. While the UH-60M is
TABLE 2 Basic Equipment List for Forward Aeromedical much more versatile for use in urban combat, the rural terrain
Resuscitative / Surgical Teams or Rotary-Wing Critical Care Air where AFRICOM operations are occurring might mitigate the
Transport Teams on a CH-47 downside of the lower maneuverability of the CH-47. Still, this
Forward Aeromedical Rotary-Wing Critical Care limitation must be considered for kinetic operations that could
Resuscitative / Surgical Team Air Transport Team arise in urban environments. Lastly, the larger equipment load
Oxygenation equipment Oxygenation equipment of these potential medical teams will affect the range of the
Anesthesia equipment Anesthesia equipment CH-47 in a similar capacity to the UH-60M, so this tradeoff
Anesthesia medications Anesthesia medications for increased casualty care capabilities must be understood.
Analgesic medications Analgesic medications
Cold-store whole blood Cold-store whole blood Conclusion
Rapid infusion devices Rapid infusion devices As the U.S. military shifts doctrinal focus towards INDOPACOM
Blood gas analyzer Blood gas analyzer while retaining SOF in AFRICOM, leadership must also es-
Hemodynamic monitoring Hemodynamic monitoring tablish an effective plan for transporting critically injured
Warming devices Warming devices casualties. Introducing the CH-47 into the U.S. aeromedical
Cricothyroidotomy set ECMO equipment evacuation strategy for SOCAF personnel would add a special-
Chest thoracostomy set Intravenous lines ized tool to the toolbox for medical evacuation, far-forward
ER thoracotomy Set Mechanical ventilators physician-augmented care provision, and critical care missions
Ultrasound machine Burn management to improve survivability. The CH-47’s larger fuselage, higher
Airway equipment maximum gross weight, and faster cruising speed have con-
REBOA catheters tributed to decreased mortality in prior use cases, addressing
ECMO = extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; ER = emergency gaps in prolonged field care to complement the UH-60M’s ca-
room; REBOA = resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the pabilities. Successful utilization of the CH-47 in AFRICOM
aorta. may even validate this capability in a lower-threat theater to
forecast its utility in LSCO scenarios. Integrating the CH-47
litters—equivalent to the UH-60M’s capability—but can be would enhance—not replace—the current medical evacuation
increased to hold four more litters in the front of the aircraft approach, offering multiple options to respond to the multi-
for eight total, in addition to transporting multiple ambula- faceted challenges of modern warfare while furthering efforts
tory patients. As a note, the CH-47’s maximum capacity of to permit zero preventable battlefield deaths.
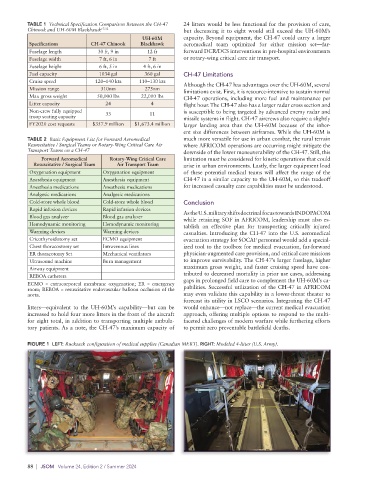
FIGURE 1 LEFT: Rucksack configuration of medical supplies (Canadian MERT). RIGHT: Modeled 4-litter (U.S. Army).
88 | JSOM Volume 24, Edition 2 / Summer 2024