Page 10 - JSOM Summer 2024
P. 10
FEATURE ARTICLES the competitive atmospheres within the military and in sport,
Advancing Combat Casualty Care Statistics and Other Battle- leaders must use creative strategies to mitigate the consequences
field Care Metrics: In this commentary, Janak and colleagues of this behavioral risk factor.
propose adjustments to traditional aggregate combat casualty Evaluation of a Rebreathing System for Use with Portable
care statistics by integrating statistics from the Department of Mechanical Ventilators: Blakeman and colleagues designed and
Defense Military Trauma Mortality Review process. To better evaluated a closed-circuit system that allows rebreathing of gases
understand the true impact of military medicine on the battle- while scrubbing carbon dioxide in conjunction with portable me-
field-injured case fatality rate (CFR), the authors recommend chanical ventilators in a bench model. The Zoll 731 and AutoMedx
integrating the CFR with two additional statistics: percentage SAVe II ventilators were employed to test the system using a range
of settings and lung models, with 1 and 3L/min low-flow oxygen
of fatalities with potentially survivable injuries and potentially into a reservoir bag. The researchers found that such a system has
preventable deaths. the potential for oxygen conservation but requires diligent mon-
An Analysis of Tube Thoracostomy in Combat: Implications itoring of inspired oxygen concentration and carbon dioxide to
for Improved Prehospital Recognition and Treatment: Fisher avoid negative consequences.
and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of the Department Rebreather system connected to a patient.
of Defense Trauma Registry (DoDTR) data set from 2007 to 2020
to identify all casualties who received a tube thoracostomy within
24 hours of admission to a military treatment facility (n=2,178).
They found that combat casualties with chest trauma often had
multiple injuries complicating prehospital and hospital care, with
explosions and gunshot wounds being the most common mech-
anisms of injury associated with tube thoracostomy, which was
often performed by enlisted medical personnel. These findings
highlight the need to understand wounding patterns and interven-
tions to anticipate prehospital care needs.
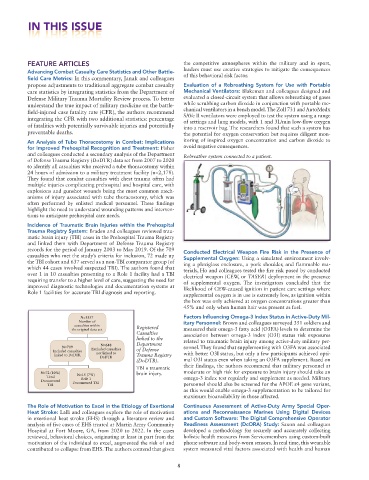
Incidence of Traumatic Brain Injuries within the Prehospital
Trauma Registry System: Braden and colleagues reviewed trau-
matic brain injury (TBI) cases in the Prehospital Trauma Registry
and linked them with Department of Defense Trauma Registry
records for the period of January 2003 to May 2019. Of the 709 Conducted Electrical Weapon Fire Risk in the Presence of
casualties who met the study’s criteria for inclusion, 72 made up Supplemental Oxygen: Using a simulated environment involv-
the TBI cohort and 637 served as a non-TBI comparator group (of ing a plexiglass enclosure, a pork shoulder, and flammable ma-
which 44 cases involved suspected TBI). The authors found that terials, Ho and colleagues tested the fire risk posed by conducted
over 1 in 10 casualties presenting to a Role 1 facility had a TBI electrical weapon (CEW, or TASER) deployment in the presence
requiring transfer to a higher level of care, suggesting the need for of supplemental oxygen. The investigators concluded that the
improved diagnostic technologies and documentation systems at likelihood of CEW-caused ignition in patient care settings where
Role 1 facilities for accurate TBI diagnosis and reporting. supplemental oxygen is in use is extremely low, as ignition within
the box was only achieved at oxygen concentrations greater than
45% and only when human hair was present as fuel.
N=1357 Factors Influencing Omega-3 Index Status in Active-Duty Mil-
Number of itary Personnel: Brown and colleagues surveyed 351 soldiers and
casualties within
the original data set Registered measured their omega-3 fatty acid (O3FA) levels to determine the
Casualties association between omega-3 index (O3I) status risk exposures
linked to the related to traumatic brain injury among active-duty military per-
N=709 N=648 Department sonnel. They found that supplementing with O3FA was associated
Included casualties Excluded casualties of Defense
linked to DoDTR not linked to Trauma Registry with better O3I status, but only a few participants achieved opti-
DoDTR
(DoDTR). mal O3I status even when taking an O3FA supplement. Based on
TBI = traumatic their findings, the authors recommend that military personnel at
N=72 (10%) N=15 (7%) brain injury. moderate or high risk for exposure to brain injury should take an
Total omega-3 index test regularly and supplement as needed. Military
Role 1
Documented Documented TBI
TBI personnel should also be screened for the APOE ε4 gene variant,
as this would enable omega-3 supplementation to be tailored for
maximum bioavailability in those affected.
The Role of Motivation to Excel in the Etiology of Exertional Continuous Assessment of Active-Duty Army Special Oper-
Heat Stroke: Lalli and colleagues explore the role of motivation ations and Reconnaissance Marines Using Digital Devices
in exertional heat stroke (EHS) through a literature review and and Custom Software: The Digital Comprehensive Operator
analysis of five cases of EHS treated at Martin Army Community Readiness Assessment (DcORA) Study: Saxon and colleagues
Hospital at Fort Moore, GA, from 2020 to 2022. In the cases developed a methodology for securely and accurately collecting
reviewed, behavioral choices, originating at least in part from the holistic health measures from Servicemembers using custom-built
motivation of the individual to excel, augmented the risk of and phone software and body-worn sensors. In real time, this wearable
contributed to collapse from EHS. The authors contend that given system measured vital factors associated with health and human
8