Page 85 - 2022 Spring JSOM
P. 85
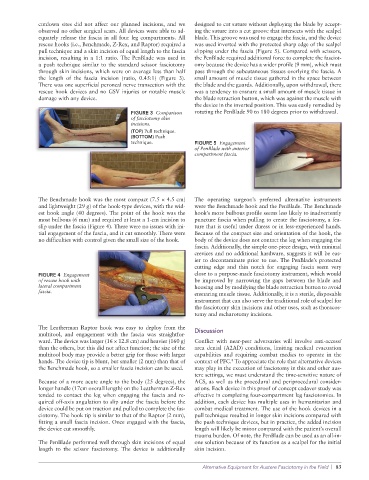
cutdown sites did not affect our planned incisions, and we designed to cut suture without deploying the blade by accept-
observed no other surgical scars. All devices were able to ad- ing the suture into a cut groove that intersects with the scalpel
equately release the fascia in all four leg compartments. All blade. This groove was used to engage the fascia, and the device
rescue hooks (i.e., Benchmade, Z-Rex, and Raptor) required a was used inverted with the protected sharp edge of the scalpel
pull technique and a skin incision of equal length to the fascia slipping under the fascia (Figure 5). Compared with scissors,
incision, resulting in a 1:1 ratio. The PenBlade was used in the PenBlade required additional force to complete the fasciot-
a push technique similar to the standard scissor fasciotomy omy because the device has a wider profile (9 mm), which must
through skin incisions, which were on average less than half pass through the subcutaneous tissues overlying the fascia. A
the length of the fascia incision (ratio, 0.45:1) (Figure 3). small amount of muscle tissue gathered in the space between
There was one superficial peroneal nerve transection with the the blade and the guards. Additionally, upon withdrawal, there
rescue hook devices and no GSV injuries or notable muscle was a tendency to ensnare a small amount of muscle tissue in
damage with any device. the blade retraction button, which was against the muscle with
the device in the inverted position. This was easily remedied by
FIGURE 3 Comparison rotating the PenBlade 90 to 180 degrees prior to withdrawal.
of fasciotomy skin
incisions.
(TOP) Pull technique.
(BOTTOM) Push
technique. FIGURE 5 Engagement
of PenBlade with anterior
compartment fascia.
The Benchmade hook was the most compact (7.5 × 4.5 cm) The operating surgeon’s preferred alternative instruments
and lightweight (29 g) of the hook-type devices, with the wid- were the Benchmade hook and the PenBlade. The Benchmade
est hook angle (40 degrees). The point of the hook was the hook’s more bulbous profile seems less likely to inadvertently
most bulbous (6 mm) and required at least a 1-cm incision to puncture fascia when pulling to create the fasciotomy, a fea-
slip under the fascia (Figure 4). There were no issues with ini- ture that is useful under duress or in less-experienced hands.
tial engagement of the fascia, and it cut smoothly. There were Because of the compact size and orientation of the hook, the
no difficulties with control given the small size of the hook. body of the device does not contact the leg when engaging the
fascia. Additionally, the simple one-piece design, with minimal
crevices and no additional hardware, suggests it will be eas-
ier to decontaminate prior to use. The PenBlade’s protected
cutting edge and thin notch for engaging fascia seem very
FIGURE 4 Engagement close to a purpose-made fasciotomy instrument, which would
of rescue hook with be improved by narrowing the gaps between the blade and
lateral compartment housing and by modifying the blade retraction button to avoid
fascia. ensnaring muscle tissue. Additionally, it is a sterile, disposable
instrument that can also serve the traditional role of scalpel for
the fasciotomy skin incisions and other uses, such as thoracos-
tomy and escharotomy incisions.
The Leatherman Raptor hook was easy to deploy from the
multitool, and engagement with the fascia was straightfor- Discussion
ward. The device was larger (16 × 12.8 cm) and heavier (160 g) Conflict with near-peer adversaries will involve anti-access/
than the others, but this did not affect function; the size of the area denial (A2AD) conditions, limiting medical evacuation
multitool body may provide a better grip for those with larger capabilities and requiring combat medics to operate in the
8
hands. The device tip is blunt, but smaller (2 mm) than that of context of PFC. To appreciate the role that alternative devices
the Benchmade hook, so a smaller fascia incision can be used. may play in the execution of fasciotomy in this and other aus-
tere settings, we must understand the time-sensitive nature of
Because of a more acute angle to the body (25 degrees), the ACS, as well as the procedural and periprocedural consider-
longer handle (17cm overall length) on the Leatherman Z-Rex ations. Each device in this proof of concept cadaver study was
tended to contact the leg when engaging the fascia and re- effective in completing four-compartment leg fasciotomies. In
quired off-axis angulation to slip under the fascia before the addition, each device has multiple uses in humanitarian and
device could be put on traction and pulled to complete the fas- combat medical treatment. The use of the hook devices in a
ciotomy. The hook tip is similar to that of the Raptor (2 mm), pull technique resulted in longer skin incisions compared with
fitting a small fascia incision. Once engaged with the fascia, the push technique devices, but in practice, the added incision
the device cut smoothly. length will likely be minor compared with the patient’s overall
trauma burden. Of note, the PenBlade can be used as an all-in-
The PenBlade performed well through skin incisions of equal one solution because of its function as a scalpel for the initial
length to the scissor fasciotomy. The device is additionally skin incision.
Alternative Equipment for Austere Fasciotomy in the Field | 83