Page 47 - 2022 Spring JSOM
P. 47
FIGURE 1 Appropriate placement 4. Observe the retinal veins for pulsations. Note the presence or ab-
of the linear probe. sence of spontaneous venous pulsations
Ultrasound gel is placed over a closed eye- 5. Repeat the step 1–4 sequence in the contralateral eye.
lid and the probe placed horizontally over
the eyelid, applying as little pressure to the The retinal vessels can be seen emerging from the optic disc. Retinal
globe as possible. If available, Tegaderm veins can be identified by their slightly larger, thicker size and darker
or other thin covering (e.g., Latex glove) color. Retinal arteries are small, thin, and lighter in color than retinal
should be placed over a closed eyelid for
further protection. veins.
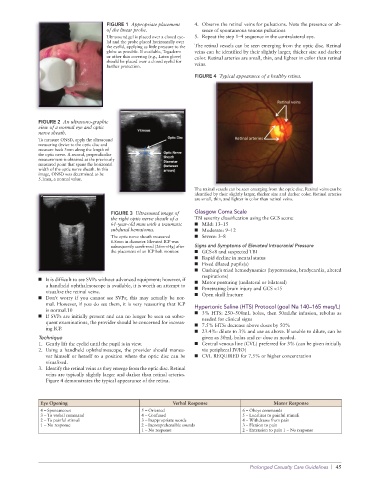
FIGURE 4 Typical appearance of a healthy retina.
FIGURE 2 An ultrasono-graphic
view of a normal eye and optic
nerve sheath.
To measure ONSD, apply the ultrasound
measuring device to the optic disc and
measure back 3mm along the length of
the optic nerve. A second, perpendicular
measurement is obtained at the previously
measured point that spans the horizontal
width of the optic nerve sheath. In this
image, ONSD was determined to be
5.1mm, a normal value.
The retinal vessels can be seen emerging from the optic disc. Retinal veins can be
identified by their slightly larger, thicker size and darker color. Retinal arteries
are small, thin, and lighter in color than retinal veins.
FIGURE 3 Ultrasound image of Glasgow Coma Scale
the right optic nerve sheath of a TBI severity classification using the GCS score:
61-year-old man with a traumatic ■ Mild: 13–15
subdural hematoma. ■ Moderate: 9–12
The optic nerve sheath measured ■ Severe: 3–8
6.8mm in diameter. Elevated ICP was
subsequently confirmed (26mmHg) after Signs and Symptoms of Elevated Intracranial Pressure
the placement of an ICP bolt monitor. ■ GCS<8 and suspected TBI
■ Rapid decline in mental status
■ Fixed dilated pupils(s)
■ Cushing’s triad hemodynamics (hypertension, bradycardia, altered
respirations)
■ It is difficult to see SVPs without advanced equipment; however, if ■ Motor posturing (unilateral or bilateral)
a handheld ophthalmoscope is available, it is worth an attempt to ■ Penetrating brain injury and GCS <15
visualize the retinal veins.
■ Don’t worry if you cannot see SVPs; this may actually be nor- ■ Open skull fracture
mal. However, if you do see them, it is very reassuring that ICP Hypertonic Saline (HTS) Protocol (goal Na 140–165 meq/L)
is normal.10
■ If SVPs are initially present and can no longer be seen on subse- ■ 3% HTS: 250–500mL bolus, then 50mL/hr infusion, rebolus as
needed for clinical signs
quent examinations, the provider should be concerned for increas- ■ 7.5% HTS: decrease above doses by 50%
ing ICP.
■ 23.4%: dilute to 3% and use as above. If unable to dilute, can be
Technique given as 30mL bolus and re- dose as needed.
1. Gently lift the eyelid until the pupil is in view. ■ Central venous line (CVL) preferred for 3% (can be given initially
2. Using a handheld ophthalmoscope, the provider should maneu- via peripheral IV/IO)
ver himself or herself to a position where the optic disc can be ■ CVL REQUIRED for 7.5% or higher concentration
visualized.
3. Identify the retinal veins as they emerge from the optic disc. Retinal
veins are typically slightly larger and darker than retinal arteries.
Figure 4 demonstrates the typical appearance of the retina.
Eye Opening Verbal Response Motor Response
4 – Spontaneous 5 – Oriented 6 – Obeys commands
3 – To verbal command 4 – Confused 5 – Localizes to painful stimuli
2 – To painful stimuli 3 – Inappropriate words 4 – Withdraws from pain
1 – No response 2 – Incomprehensible sounds 3 – Flexion to pain
1 – No response 2 – Extension to pain 1 – No response
Prolonged Casualty Care Guidelines | 45