Page 48 - JSOM Fall 2021
P. 48
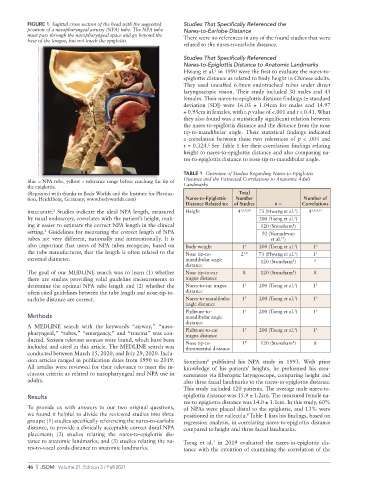
FIGURE 1 Sagittal cross section of the head with the suggested Studies That Specifically Referenced the
position of a nasopharyngeal airway (NPA) tube. The NPA tube Nares-to-Earlobe Distance
must pass through the nasopharyngeal space and go beyond the There were no references in any of the found studies that were
base of the tongue, but not touch the epiglottis.
related to the nares-to-earlobe distance.
Studies That Specifically Referenced
Nares-to-Epiglottis Distance to Anatomic Landmarks
Hwang et al. in 1990 were the first to evaluate the nares-to-
1
epiglottis distance as related to body height in Chinese adults.
They used uncuffed 6.0mm endotracheal tubes under direct
laryngoscopic vision. Their study included 30 males and 43
females. Their nares-to-epiglottis distance findings (± standard
deviation [SD]) were 16.03 ± 1.04cm for males and 14.97
± 0.95cm in females, with a p value of <.001 and r = 0.41. What
they also found was a statistically significant relation between
the nares-to-epiglottis distance and the distance from the nose
tip-to-mandibular angle. Their statistical findings indicated
a correlation between these two references of p < .004 and
r = 0.324. See Table 1 for their correlation findings relating
1
height to nares-to-epiglottis distance and also comparing na-
res-to-epiglottis distance to nose-tip-to-mandibular angle.
TABLE 1 Overview of Studies Regarding Nares-to-Epiglottis
blue = NPA tube, yellow = tolerance range before reaching the tip of Distance and the Extracted Correlations to Anatomic Adult
the epiglottis. Landmarks
(Reprinted with thanks to Body Worlds and the Institute for Plastina- Total
tion, Heidelberg, Germany; www.bodyworlds.com) Nares-to-Epiglottis Number Number of
Distance Related to: of Studies n = Correlations
2
1
inaccurate. Studies indicate the ideal NPA length, measured Height 4 1,3,8,11 73 (Hwang et al. ) 4 1,3,8,11
by nasal endoscopy, correlates with the patient’s height, mak- 200 (Tseng et al. )
3
ing it easier to estimate the correct NPA length in the clinical 120 (Stoneham )
8
setting. Guidelines for measuring the correct length of NPA 50 (Vamadevan
2
tubes are very different, nationally and internationally. It is et al. )
11
also important that users of NPA tubes recognize, based on Body weight 1 3 200 (Tseng et al. ) 1 3
3
the tube manufacturer, that the length is often related to the Nose tip-to- 2 1,8 73 (Hwang et al. ) 1 1
1
external diameter. mandibular angle 120 (Stoneham ) 8
8
distance
The goal of our MEDLINE search was to learn (1) whether Nose tip-to-ear 8 120 (Stoneham ) 8
8
there are studies providing valid guideline measurements to tragus distance
determine the optimal NPA tube length and (2) whether the Nares-to-ear tragus 1 3 200 (Tseng et al. ) 1 3
3
often cited guidelines between the tube length and nose-tip-to- distance
3
earlobe distance are correct. Nares-to-mandibular 1 3 200 (Tseng et al. ) 1 3
angle distance
Philtrum-to- 1 3 200 (Tseng et al. ) 1 3
3
Methods mandibular angle
distance
A MEDLINE search with the keywords “airway,” “naso- 3 3 3
pharyngeal,” “tubes,” “emergency,” and “trauma” was con- Philtrum-to-ear 1 200 (Tseng et al. ) 1
tragus distance
ducted. Sixteen relevant sources were found, which have been 8 8
included and cited in this article. The MEDLINE search was Nose tip-to- 1 120 (Stoneham ) 8
thyromental distance
conducted between March 15, 2020, and July 29, 2020. Inclu-
sion articles ranged in publication dates from 1990 to 2019. Stoneham published his NPA study in 1993. With prior
8
All articles were reviewed for their relevance to meet the in- knowledge of his patients’ heights, he performed his mea-
clusion criteria as related to nasopharyngeal and NPA use in surements via fiberoptic laryngoscope, comparing height and
adults. also three facial landmarks to the nares-to-epiglottis distance.
This study included 120 patients. The average male nares-to-
Results epiglottis distance was 15.9 ± 1.2cm. The measured female na-
res-to-epiglottis distance was 14.0 ± 1.1cm. In this study, 60%
To provide us with answers to our two original questions, of NPAs were placed distal to the epiglottis, and 13% were
we found it helpful to divide the reviewed studies into three positioned in the vallecula. Table 1 lists his findings, based on
8
groups: (1) studies specifically referencing the nares-to- earlobe regression analysis, in correlating nares-to-epiglottis distance
distance, to provide a clinically acceptable correct distal NPA compared to height and three facial landmarks.
placement; (2) studies relating the nares-to-epiglottis dis-
tance to anatomic landmarks; and (3) studies relating the na- Tseng et al. in 2019 evaluated the nares-to-epiglottis dis-
3
res-to-vocal cords distance to anatomic landmarks. tance with the intention of examining the correlation of the
46 | JSOM Volume 21, Edition 3 / Fall 2021