Page 51 - JSOM Summer 2020
P. 51
(such as a bite), through open wounds on the skin or inside of the Regionally Specific Snakebite Treatment
mouth, or by ingestion (such as drinking a glass of venom with for Each Combatant Command
an ulcer). If a significant amount of venom enters the bloodstream Whenever possible, broad-spectrum, field-stable antivenoms are
through an open wound and produces typical symptoms of a snake- recommended to enable syndromic diagnosis and treatment at the
bite, it is treated with antivenom like any other envenomation. For point of injury without the need to identify the species responsible
ocular exposure alone without signs of systemic envenomation, an- for the bite. Citations of the relevant literature on safety, efficacy,
tivenom is not indicated and the management is like any ocular and dosing for each product are provided at the end of Appendix B.
chemical exposure with copious irrigation. Spitting cobras can also
deliver a venomous bite, so it is important to rule out an actual Determine the appropriate first line antivenom for your area of
snakebite in patients who have encountered one of these snakes. operations prior to deployment using this section, then refer back
to the Universal Approach to Snakebite Assessment, Diagnosis,
Signs and Symptoms: Immediate signs and symptoms of venom and Treatment on page 44 for detailed instructions and a stepwise
ophthalmia include intense local pain, swelling and/or spasms of approach to snakebite management throughout the course of care.
156
the eyelid, lacrimation, and leukorrhea. The primary concern is Abbreviated antivenom guidelines for each regional combatant
corneal epithelial injury which can lead to blindness by secondary command are included below.
infection or scarring if not treated correctly. 7,25,54,156–158 Treatment
of venom ophthalmia is relatively simple and similar to managing AFRICOM – Abbreviated Treatment Guidelines
a patient who has been splashed in the eyes with a harmful chem- Safe and effective broad-spectrum, field-stable antivenoms are
ical solution.
available for all three syndromes of snake envenomation in this
First Aid: Confirm that the patient did not experience a snakebite AOR and treatment does not require identification of the species
in addition to the ophthalmia. Immediately irrigate the eye with responsible. Snakebite treatment at the point of injury is recom-
copious quantities of water, normal saline, or a bland fluid such as mended for AFRICOM due to prolonged evacuation times, high
milk if nothing else is available. Remove clothing and decontami- incidence of snakebites, and the high risk of death or permanent
nate the patient from head to toe with soap and water to prevent disability from many venomous snakes in the AOR if early an-
second re-exposure to dried venom. 54 tivenom treatment is not available.
1. First line (AFRICOM–SUB-SAHARAN AFRICA):
Clinical Management: Apply topical anesthetic eye drops (tetra- POLYSERP-P
caine) to facilitate thorough irrigation and examination of the a. FIELD-STABLE. BROAD-SPECTRUM COVERAGE FOR
affected eyes. Irrigate the eyes thoroughly using water or normal 24+ SPECIES CYTO/HEMO/NEURO.
saline for ≥ 15 minutes. 156
b. Single-source treatment option for all neurotoxic, hemo-
Fluorescein Stain and Examination Using a Slit Lamp or Ophthal- toxic, and cytotoxic snake envenomations in sub-Saharan
moscope for Corneal Injury: If present, treat with antimicrobial Africa when the causative species is either unknown or
eye drops (such as tetracycline and chloramphenicol) or ointments among the 24 snakes for which this product is directly indi-
and mydriatics. Reassess daily with slit lamp examination. If ab- cated. Only polyvalent to include boomslangs and only an-
sent, consider benefits vs risks of antimicrobial eye drops. tivenom for mole viper envenomations. Directly or indirectly
covers all of the WHO category 1 and category 2 snakes in
Additional Treatments to Consider: Topical eye drops containing this region for which an antivenom currently exists.
either epinephrine (1:1000) or phenylephrine (10%) are reported c. Initial dose = 6 vials all syndromes, additional doses = 2
to immediately relieve the burning sensation produced by the vials as needed.
venom. 54,156
2. First line (AFRICOM–NORTH AFRICA): POLYSERP-M
Contraindicated Treatments: Antivenom (topical or systemic) is not a. FIELD-STABLE. BROAD-SPECTRUM COVERAGE FOR
indicated for patients with ocular exposure to snake venom. 54,156,159 27+ SPECIES CYTO/HEMO/NEURO.
Topical steroids are contraindicated for these patients.
AFRICA COMMAND – FIRST LINE ANTIVENOMS
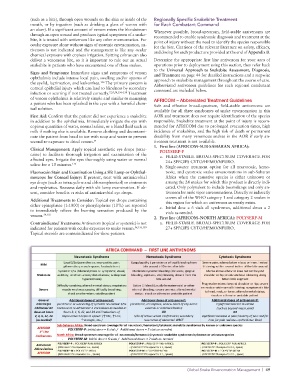
Neurotoxic Syndrome Hemotoxic Syndrome Cytotoxic Syndrome
Local S/Sx (paresthesias; neuropathic pain; Coagulopathy ± persistence of local bleeding from Severe pain; edema below elbow or knee; limited
Mild
piloerection; muscle spasm, fasciculations) bite wound > 30 mins after bite blistering within several inches of the bite wound
Systemic S/Sx (bilateral ptosis GI symptoms; visual, Moderate systemic bleeding (old scabs, gingival Edema above elbow or knee but not beyond
Moderate auditory, or other sensory disturbances; widespread bleeding, epistaxis, etc); bruising distant from the shoulder or hip; moderate local blistering along
hyperesthesia) bite wound bitten limb segment
Progressive edema beyond shoulder or hip; severe
Difficulty speaking; altered mental status; respiratory Active GI bleed (usually hematemesis) or other
Severe muscle weakness causing difficulty breathing; internal bleeding; severe anemia; altered mental necrosis or widespread blistering; symptomatic bite
to head, neck, or torso; altered mental status;
shock or otherwise unstable patient status; shock or otherwise unstable patient
shock or otherwise unstable patient
General Additional doses of antivenom if: Additional doses of antivenom if: Additional doses of antivenom if:
Criteria for persistence or worsening of systemic neurotoxic S/Sx. persistence, resumption, or new onset of any active significant increase in edema
additional AV Continue to re-administer 2 vial boluses as needed at external or internal bleeding (such as beyond major joint)
doses at hours hours 2, 4, 6, 12, and 24 until indications of OR OR
2, 4, 6, 12, 24 improvement begin to appear (↑SBC, ↑LOC, S/Sx of active venom confirmed by secondary significant increase in pain (severity of pain and/or
(as needed) ↑strength, etc.) recurrence of abnormal WBCT how far pain radiates up the bitten limb)
Sub-Saharan Africa: Broad-spectrum coverage for all neurotoxic/hemotoxic/cytotoxic snakebite syndromes by known or unknown species
AFRICOM - POLYSERP-P: Initial dose = 6 vials / Additional doses = 2 vials as needed
st
1 Line
Antivenoms North Africa: Broad-spectrum coverage for all neurotoxic/hemotoxic/cytotoxic snakebite syndromes by known or unknown species
- POLYSERP-M: Initial dose = 6 vials / Additional doses = 2 vials as needed
Antivenom POLYSERP-P = POLYSERP PAN-AFRICA POLYSERP-P = POLYSERP PAN-AFRICA POLYSERP-P = POLYSERP PAN-AFRICA
Abbreviations - (POLYSERP Therapeutics S.L, Spain) - (POLYSERP Therapeutics S.L, Spain) - (POLYSERP Therapeutics S.L, Spain)
POLYSERP-M = POLYSERP MENA
POLYSERP-M = POLYSERP MENA
POLYSERP-M = POLYSERP MENA
AFRICOM - (POLYSERP Therapeutics S.L., Spain) - (POLYSERP Therapeutics S.L., Spain) - (POLYSERP Therapeutics S.L., Spain)
Global Snake Envenomation Management | 49