Page 121 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Fall 2015
P. 121
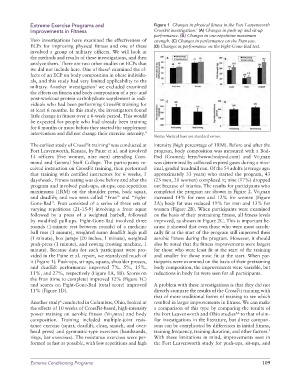
Extreme Exercise Programs and Figure 1 Changes in physical fitness in the Fort Leavenworth
5
Improvements in Fitness CrossFit investigation. (A) Changes in push-up and sit-up
performance. (B) Changes in one-repetition maximum
Two investigations have examined the effectiveness of strength. (C) Changes in performance on the Fran test.
ECPs for improving physical fitness and one of these (D) Changes in performance on the Fight-Gone-Bad test.
involved a group of military officers. We will look at
the methods and results of these investigations, and then
analyze them. There are two other studies on ECPs that
2
we did not include here. One of these examined the ef-
fects of an ECP on body composition in obese individu-
als, and this study had very limited applicability to the
3
military. Another investigation we excluded examined
the effects on fitness and body composition of a pre- and
post-workout protein-carbohydrate supplement in indi-
viduals who had been performing CrossFit training for
at least 6 months. In this study, the investigators found
little change in fitness over a 6-week period. This would
be expected for people who had already been training
for 6 months or more before they started the supplement
intervention and did not change their exercise intensity. 4
Notes: Vertical bars are standard errors.
The earliest study of CrossFit training was conducted at intensity (high percentage of 1RM). Before and after the
5
Fort Leavenworth, Kansas, by Paine et al. and involved program, body composition was measured with a Bod-
14 officers (five women, nine men) attending Com- Pod (Cosmed; http://www.bodpod.com) and Vo max
2
mand and General Staff College. The participants re- was determined by collected expired gases during a max-
ceived instruction on CrossFit training, then performed imal, graded treadmill run. Of the 54 adults (average age:
that training with certified instructors for 6 weeks, 5 approximately 33 years) who started the program, 43
days/week. Fitness testing was done before and after the (23 men, 20 women) completed it; nine (17%) dropped
program and involved push-ups, sit-ups; one-repetition out because of injuries. The results for participants who
maximums (1RM) on the shoulder press, back squat, completed the program are shown in Figure 2. Vo max
2
and deadlift; and two tests called “Fran” and “Fight- increased 14% for men and 12% for women (Figure
Gone-Bad”. Fran consisted of a series of three sets of 2A); body fat was reduced 19% for men and 13% for
varying repetitions (21-15-9) involving a front squat women (Figure 2B). When participants were examined
followed by a press of a weighted barbell, followed on the basis of their pretraining fitness, all fitness levels
by modified pull-ups. Fight-Gone-Bad involved three improved, as shown in Figure 2C. This is important be-
rounds (1-minute rest between rounds) of a medicine cause it showed that even those who were most aerobi-
ball toss (1 minute), weighted sumo deadlift high pull cally fit at the start of the program still improved their
(1 minute), box jumps (20 inches, 1 minute), weighted aerobic fitness during the program. However, it should
push-press (1 minute), and rowing (rowing machine, 1 also be noted that the fitness improvements were largest
minute). Because data for each participant were pro- for those who were least fit at the start of the training
vided in the Paine et al. report, we reanalyzed much of and smaller for those most fit at the start. When par-
it (Figure 1). Push-ups, sit-ups, squats, shoulder presses, ticipants were examined on the basis of their pretraining
and deadlift performance improved 7%, 5%, 15%, body composition, the improvements were variable, but
11%, and 27%, respectively (Figure 1A, 1B). Scores on reductions in body fat were seen for all participants.
the Fran (time to complete) improved 12% (Figure 1C)
and scores on Fight-Gone-Bad (total score) improved A problem with these investigations is that they did not
11% (Figure 1D). directly compare the results of the CrossFit training with
that of more traditional forms of training to see which
6
Another study conducted in Columbus, Ohio, looked at resulted in larger improvements in fitness. We can make
the effects of 10 weeks of CrossFit-based, high-intensity a comparison of this type by comparing the results of
power training on aerobic fitness (Vo max) and body the Fort Leavenworth and Ohio studies to that of sim-
5,6
2
composition. Training included multiple-joint resis- ilar investigations in the literature, but direct compari-
tance exercise (squat, deadlift, clean, snatch, and over- sons can be complicated by differences in initial fitness,
head press) and gymnastic-type exercises (handstands, training frequency, training duration, and other factors.
7
rings, bar exercises). The resistance exercises were per- With these limitations in mind, improvements seen in
formed as fast as possible, with low repetitions and high the Fort Leavenworth study for push-ups, sit-ups, and
Extreme Conditioning Programs 109