Page 87 - PJ MED OPS Handbook 8th Ed
P. 87
Management:
1. Antacid of choice, can be Rolaids or Tums type meds
2. Famotidine (Pepcid) 20mg PO bid
3. PO hydration
DISPOSITION:
1. Evacuation for worsening.
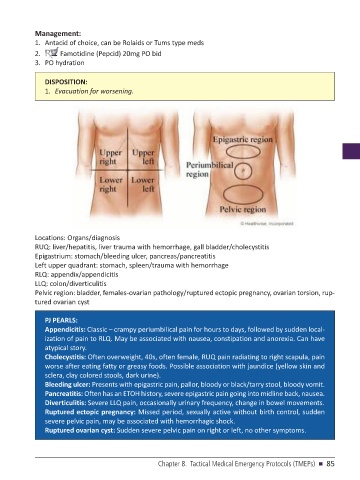
Locations: Organs/diagnosis
RUQ: liver/hepatitis, liver trauma with hemorrhage, gall bladder/cholecystitis
Epigastrium: stomach/bleeding ulcer, pancreas/pancreatitis
Left upper quadrant: stomach, spleen/trauma with hemorrhage
RLQ: appendix/appendicitis
LLQ: colon/diverticulitis
Pelvic region: bladder, females-ovarian pathology/ruptured ectopic pregnancy, ovarian torsion, rup-
tured ovarian cyst
PJ PEARLS:
Appendicitis: Classic – crampy periumbilical pain for hours to days, followed by sudden local-
ization of pain to RLQ. May be associated with nausea, constipation and anorexia. Can have
atypical story.
Cholecystitis: Often overweight, 40s, often female, RUQ pain radiating to right scapula, pain
worse after eating fatty or greasy foods. Possible association with jaundice (yellow skin and
sclera, clay colored stools, dark urine).
Bleeding ulcer: Presents with epigastric pain, pallor, bloody or black/tarry stool, bloody vomit.
Pancreatitis: Often has an ETOH history, severe epigastric pain going into midline back, nausea.
Diverticulitis: Severe LLQ pain, occasionally urinary frequency, change in bowel movements.
Ruptured ectopic pregnancy: Missed period, sexually active without birth control, sudden
severe pelvic pain, may be associated with hemorrhagic shock.
Ruptured ovarian cyst: Sudden severe pelvic pain on right or left, no other symptoms.
Chapter 8. Tactical Medical Emergency Protocols (TMEPs) n 85