Page 217 - PJ MED OPS Handbook 8th Ed
P. 217
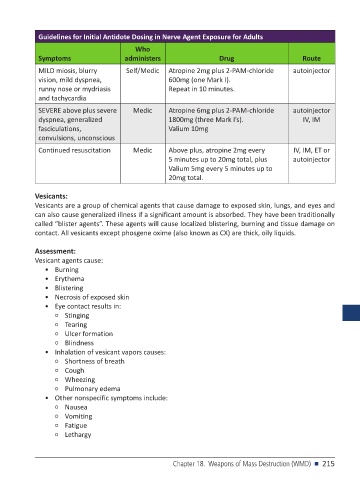
Guidelines for Initial Antidote Dosing in Nerve Agent Exposure for Adults
Who
Symptoms administers Drug Route
MILD miosis, blurry Self/Medic Atropine 2mg plus 2-PAM-chloride autoinjector
vision, mild dyspnea, 600mg (one Mark I).
runny nose or mydriasis Repeat in 10 minutes.
and tachycardia
SEVERE above plus severe Medic Atropine 6mg plus 2-PAM-chloride autoinjector
dyspnea, generalized 1800mg (three Mark I’s). IV, IM
fasciculations, Valium 10mg
convulsions, unconscious
Continued resuscitation Medic Above plus, atropine 2mg every IV, IM, ET or
5 minutes up to 20mg total, plus autoinjector
Valium 5mg every 5 minutes up to
20mg total.
Vesicants:
Vesicants are a group of chemical agents that cause damage to exposed skin, lungs, and eyes and
can also cause generalized illness if a significant amount is absorbed. They have been traditionally
called “blister agents”. These agents will cause localized blistering, burning and tissue damage on
contact. All vesicants except phosgene oxime (also known as CX) are thick, oily liquids.
Assessment:
Vesicant agents cause:
• Burning
• Erythema
• Blistering
• Necrosis of exposed skin
• Eye contact results in:
○ Stinging
○ Tearing
○ Ulcer formation
○ Blindness
• Inhalation of vesicant vapors causes:
○ Shortness of breath
○ Cough
○ Wheezing
○ Pulmonary edema
• Other nonspecific symptoms include:
○ Nausea
○ Vomiting
○ Fatigue
○ Lethargy
Chapter 18. Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) n 215