Page 175 - PJ MED OPS Handbook 8th Ed
P. 175
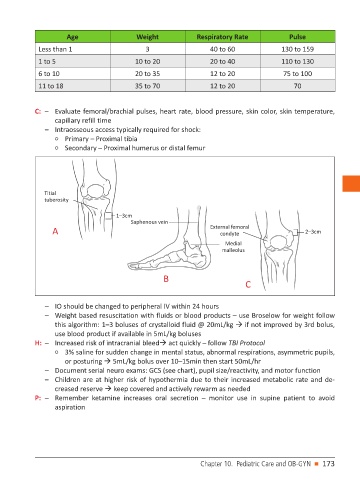
Age Weight Respiratory Rate Pulse
Less than 1 3 40 to 60 130 to 159
1 to 5 10 to 20 20 to 40 110 to 130
6 to 10 20 to 35 12 to 20 75 to 100
11 to 18 35 to 70 12 to 20 70
C: – Evaluate femoral/brachial pulses, heart rate, blood pressure, skin color, skin temperature,
capillary refill time
– Intraosseous access typically required for shock:
○ Primary – Proximal tibia
○ Secondary – Proximal humerus or distal femur
Titial
tuberosity
1–3cm
Saphenous vein
A External femoral 2–3cm
condyte
Medial
malleolus
B
C
– IO should be changed to peripheral IV within 24 hours
– Weight based resuscitation with fluids or blood products – use Broselow for weight follow
this algorithm: 1–3 boluses of crystalloid fluid @ 20mL/kg if not improved by 3rd bolus,
use blood product if available in 5mL/kg boluses
H: – Increased risk of intracranial bleed act quickly – follow TBI Protocol
○ 3% saline for sudden change in mental status, abnormal respirations, asymmetric pupils,
or posturing 5mL/kg bolus over 10–15min then start 50mL/hr
– Document serial neuro exams: GCS (see chart), pupil size/reactivity, and motor function
– Children are at higher risk of hypothermia due to their increased metabolic rate and de-
creased reserve keep covered and actively rewarm as needed
P: – Remember ketamine increases oral secretion – monitor use in supine patient to avoid
aspiration
Chapter 10. Pediatric Care and OB-GYN n 173