Page 56 - JSOM Fall 2024
P. 56
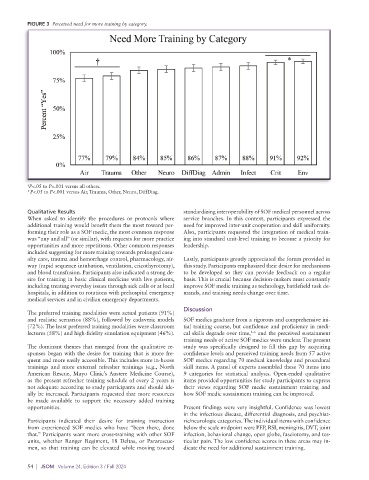
FIGURE 3 Perceived need for more training by category.
† P<.05 to P<.001 versus all others.
*P<.05 to P<.001 versus Air, Trauma, Other, Neuro, DiffDiag.
Qualitative Results standardizing interoperability of SOF medical personnel across
When asked to identify the procedures or protocols where service branches. In this context, participants expressed the
additional training would benefit them the most toward per- need for improved inter-unit cooperation and skill uniformity.
forming their role as a SOF medic, the most common response Also, participants requested the integration of medical train-
was “any and all” (or similar), with requests for more practice ing into standard unit-level training to become a priority for
opportunities and more repetitions. Other common responses leadership.
included suggesting for more training towards prolonged casu-
alty care, trauma and hemorrhage control, pharmacology, air- Lastly, participants greatly appreciated the forum provided in
way (rapid sequence intubation, ventilation, cricothyrotomy), this study. Participants emphasized their desire for mechanisms
and blood transfusion. Participants also indicated a strong de- to be developed so they can provide feedback on a regular
sire for training in basic clinical medicine with live patients, basis. This is crucial because decision-makers must constantly
including treating everyday issues through sick calls or at local improve SOF medic training as technology, battlefield task de-
hospitals, in addition to rotations with prehospital emergency mands, and training needs change over time.
medical services and in civilian emergency departments.
Discussion
The preferred training modalities were actual patients (91%)
and realistic scenarios (88%), followed by cadaveric models SOF medics graduate from a rigorous and comprehensive ini-
(72%). The least preferred training modalities were classroom tial training course, but confidence and proficiency in medi-
2–6
lectures (58%) and high-fidelity simulation equipment (46%). cal skills degrade over time, and the perceived sustainment
training needs of active SOF medics were unclear. The present
The dominant themes that emerged from the qualitative re- study was specifically designed to fill this gap by acquiring
sponses began with the desire for training that is more fre- confidence levels and perceived training needs from 57 active
quent and more easily accessible. This includes more in-house SOF medics regarding 70 medical knowledge and procedural
trainings and more external refresher trainings (e.g., North skill items. A panel of experts assembled these 70 items into
American Rescue, Mayo Clinic’s Austere Medicine Course), 9 categories for statistical analysis. Open-ended qualitative
as the present refresher training schedule of every 2 years is items provided opportunities for study participants to express
not adequate according to study participants and should ide- their views regarding SOF medic sustainment training and
ally be increased. Participants requested that more resources how SOF medic sustainment training can be improved.
be made available to support the necessary added training
opportunities. Present findings were very insightful. Confidence was lowest
in the infectious disease, differential diagnosis, and psychiat-
Participants indicated their desire for training instruction ric/neurologic categories. The individual items with confidence
from experienced SOF medics who have “been there, done below the scale midpoint were PEP, RSI, meningitis, DVT, joint
that.” Participants want more cross-training with other SOF infection, behavioral change, open globe, fasciotomy, and tes-
units, whether Ranger Regiment, 18 Deltas, or Pararescue- ticular pain. The low confidence scores in these areas may in-
men, so that training can be elevated while moving toward dicate the need for additional sustainment training.
54 | JSOM Volume 24, Edition 3 / Fall 2024