Page 21 - JSOM Fall 2023
P. 21
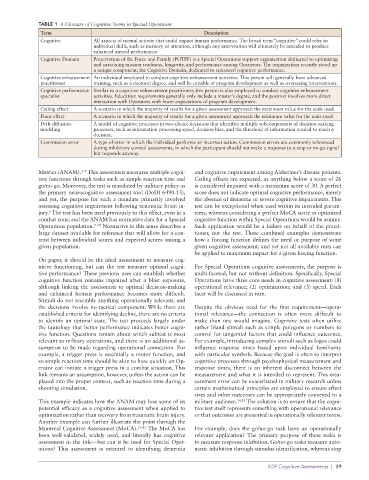
TABLE 1 A Glossary of Cognitive Terms in Special Operations
Term Description
Cognitive All aspects of mental activity that could impact human performance. The broad term “cognitive” could refer to
individual skills, such as memory or attention, although any intervention will ultimately be intended to produce
enhanced mental performance.
Cognitive Domain Preservation of the Force and Family (POTFF) is a Special Operations support organization dedicated to optimizing
and sustaining mission readiness, longevity, and performance among Operators. The organization recently stood up
a unique component, the Cognitive Domain, dedicated to enhanced cognitive performance.
Cognitive enhancement An individual employed to conduct cognitive enhancement activities. This person will generally have advanced
practitioner training, such as a doctoral degree, and will be capable of program development as well as overseeing interventions.
Cognitive performance Similar to a cognitive enhancement practitioner, this person is also employed to conduct cognitive enhancement
specialist activities. Education requirements generally only include a master’s degree, and the position involves more direct
interaction with Operators with fewer expectations of program development.
Ceiling effect A scenario in which the majority of results for a given assessment approach the maximum value for the scale used.
Floor effect A scenario in which the majority of results for a given assessment approach the minimum value for the scale used.
Drift diffusion A model of cognitive processes in two-choice decisions that identifies multiple subcomponents of decision-making
modeling processes, such as information processing speed, decision bias, and the threshold of information needed to reach a
decision.
Commission error A type of error in which the individual performs an incorrect action. Commission errors are commonly referenced
during inhibitory control assessments, in which the participant should not make a response to a stop or no-go signal
but responds anyway.
Metrics (ANAM). This assessment measures multiple cogni- and cognitive impairment among Alzheimer’s disease patients.
2–5
tive functions through tasks such as simple reaction time and Ceiling effects are expected, as anything below a score of 26
go/no-go. Moreover, the test is mandated by military policy as is considered impaired with a maximum score of 30. A perfect
the primary neurocognitive assessment tool (DoDI 6490.13), score does not indicate optimal cognitive performance, merely
and yet, the purpose for such a mandate primarily involved the absence of dementia or severe cognitive impairments. This
assessing cognitive impairment following traumatic brain in- test can be exceptional when used within its intended param-
jury. The test has been used previously to this effect, even in a eters, whereas considering a perfect MoCA score as optimized
6
combat zone, and the ANAM has normative data for a Special cognitive function within Special Operations would be asinine.
Operations population. 7–10 Normative in this sense describes a Such application would be a failure on behalf of the practi-
large dataset available for reference that will allow for a con- tioner, not the test. These combined examples demonstrate
trast between individual scores and expected scores among a how a forcing function defines the need or purpose of some
given population. given cognitive assessment, and yet not all available tests can
be applied to maximum impact for a given forcing function.
On paper, it should be the ideal assessment to measure cog-
nitive functioning, but can the test measure optimal cogni- For Special Operations cognitive assessments, the purpose is
tive performance? These previous uses can establish whether multi-faceted, but not without definition. Specifically, Special
cognitive function remains impaired after a blast exposure, Operations have three core needs in cognitive assessment: (1)
although linking the assessment to optimal decision-making operational relevance; (2) optimization; and (3) speed. Each
and enhanced human performance becomes more difficult. facet will be discussed in turn.
Stimuli do not resemble anything operationally relevant, and
the decisions involve no tactical component. While there are Despite the obvious need for the first requirement—opera-
established criteria for identifying decline, there are no criteria tional relevance—the connection is often more difficult to
to identify an optimal state. The test proceeds largely under make than one would imagine. Cognitive tests often utilize
the tautology that better performance indicates better cogni- rather bland stimuli such as simple polygons or numbers to
tive function. Questions remain about which subtest is most control for tangential factors that could influence outcomes.
relevant to military operations, and there is an additional as- For example, introducing complex stimuli such as logos could
sumption to be made regarding operational connection. For influence response times based upon individual familiarity
example, a trigger press is essentially a motor function, and with particular symbols. Because the goal is often to interpret
so simple reaction time should be akin to how quickly an Op- cognitive processes through psychophysical measurement and
erator can initiate a trigger press in a combat situation. This response times, there is an inherent disconnect between the
link remains an assumption, however, unless the action can be measurement and what it is intended to represent. This mea-
placed into the proper context, such as reaction time during a surement error can be exacerbated in military research unless
shooting simulation. certain mathematical principles are employed to ensure effect
sizes and other outcomes can be appropriately conveyed to a
This example indicates how the ANAM may lose some of its military audience. 14,15 The solution is to ensure that the cogni-
potential efficacy as a cognitive assessment when applied to tive test itself represents something with operational relevance
optimization rather than recovery from traumatic brain injury. or that outcomes are presented in operationally relevant terms.
Another example can further illustrate the point through the
Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA). 11–13 The MoCA has For example, does the go/no-go task have an operationally
been well-validated, widely used, and literally has cognitive relevant application? The primary purpose of these tasks is
assessment in the title—but can it be used for Special Oper- to measure response inhibition. Go/no-go tasks measure auto-
ations? This assessment is oriented to identifying dementia matic inhibition through stimulus identification, whereas stop
SOF Cognitive Assessments | 19