Page 69 - JSOM Fall 2019
P. 69
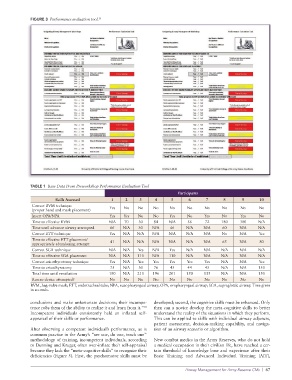
FIGURE 3 Performance evaluation tool. 13
TABLE 1 Raw Data From Preworkshop Performance Evaluation Tool
Participants
Skills Assessed 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Correct BVM technique Yes No No No No No No No No No
(proper hand and mask placement)
Insert OPA/NPA Yes Yes No No Yes No Yes No Yes No
Time to effective BVM N/A 70 30 84 N/A 56 72 180 300 N/A
Time until advance airway attempted 66 N/A 30 N/A 46 N/A N/A 60 N/A N/A
Correct ETT technique Yes N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A No N/A Yes
Time to effective ETT placement/ 41 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 65 N/A 80
appropriately abandoning attempt
Correct SGA technique N/A N/A Yes N/A Yes N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Time to effective SGA placement N/A N/A 110 N/A 110 N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Correct cricothyrotomy technique Yes N/A Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes N/A N/A Yes
Time to cricothyrotomy 75 N/A 30 76 45 44 45 N/A N/A 150
Total time until ventilation 190 N/A 210 196 201 150 135 N/A N/A 150
Rescue device attempted? No No No No No No No No No No
BVM, bag-valve mask; ETT, endotracheal tube; NPA, nasopharyngeal airway; OPA, oropharyngeal airway; SGA, supraglottic airway. Time given
in seconds.
conclusions and make unfortunate decisions; their incompe- developed; second, the cognitive skills must be enhanced. Only
tence robs them of the ability to realize it and learn from it.” then can a novice develop the meta-cognitive skills to better
10
Incompetent individuals consistently held an inflated self- understand the reality of the situations in which they perform.
appraisal of their skills or performance. This can be applied to skills with individual airway adjuncts,
patient assessment, decision-making capability, and naviga-
After observing a competent individual’s performance, as is tion of an airway scenario or algorithm.
common practice in the Army’s “see one, do one, teach one”
methodology of training, incompetent individuals, according New combat medics in the Army Reserves, who do not hold
to Dunning and Kruger, often over-inflate their self-appraisal a medical occupation in their civilian life, have reached a cer-
because they lack the “meta-cognitive skills” to recognize their tain threshold of knowledge base and experience after their
deficiencies (Figure 5). First, the psychomotor skills must be Basic Training and Advanced Individual Training (AIT),
Airway Management for Army Reserve CMs | 67