Page 50 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Fall 2016
P. 50
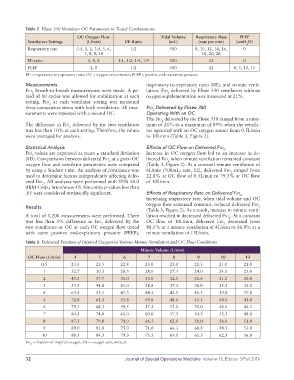
Table 2 Elisée 350 Ventilator OC Parameters in Tested Combinations
OC Oxygen Flow Tidal Volume Respiratory Rate PEEP
Ventilators Settings (L/min) I/E Ratio (mL) (rate per min) (cmH O)
2
Respiratory rate 0.5, 1, 2, 3,4, 5, 6, 1:2 500 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 0
7, 8, 9, 10 18, 20, 26
I/E ratio 2, 4, 8 1:1, 1:2, 1:4, 1:9 500 12 0
PEEP 2, 8 1:2 500 12 0, 5, 10, 15
I/E = inspiratory-to-expiratory ratio; OC = oxygen concentrator; PEEP = positive end-expiratory pressure.
Measurements inspiratory-to-expiratory ratio (I/E), and minute venti-
Fio breath-to-breath measurements were made. A pe- lation. Fio delivered by Elisée 350 ventilators without
2
2
riod of 10 cycles was allowed for stabilization at each oxygen supplementation was measured at 21%.
setting. Fio at each ventilator setting was measured
2
three consecutive times with both ventilators. All mea- Fio Delivered by Elisée 350
2
surements were repeated with a second OC. Operating With an OC
The Fio delivered by the Elisée 350 ranged from a mini-
2
The difference in Fio delivered by the two ventilators mum of 21% to a maximum of 89% when the ventila-
2
was less than 10% at each setting. Therefore, the values tor operated with an OC oxygen source from 0.5L/min
were averaged for analysis. to 10L/min (Table 3, Figure 2).
Statistical Analysis Effects of OC Flow on Delivered Fio 2
Fio values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation Increase in OC oxygen flow led to an increase in de-
2
(SD). Comparisons between delivered Fio at a given OC livered Fio when minute ventilation remained constant
2
2
oxygen flow and ventilator parameters were compared (Table 3, Figure 2). At a constant minute ventilation of
by using a Student t test. An analysis of covariance was 6L/min (500mL; rate, 12), delivered Fio ranged from
2
used to determine factors independently affecting deliv- 22.8% at OC flow of 0.5L/min to 79.3% at OC flow
ered Fio . All analyses were performed with SPSS 20.0 of 10L/min.
2
(IBM Corp.; http://www-01.ibm.com); p-values less than
.05 were considered statistically significant. Effects of Respiratory Rate on Delivered Fio 2
Increasing respiratory rate, when tidal volume and OC
oxygen flow remained constant, reduced delivered Fio
Results 2
(Table 3, Figure 2). As a result, increase in minute venti-
A total of 1,200 measurements were performed. There lation resulted in decreased delivered Fio . At a constant
2
was less than 5% difference in Fio delivered by the OC flow of 10L/min, delivered Fio decreased from
2
2
two ventilators or OC at each OC oxygen flow tested 88.5% at a minute ventilation of 4L/min to 56.8% at a
with same positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), minute ventilation of 13L/min.
Table 3 Delivered Fraction of Inspired Oxygen in Various Minute Ventilation and OC Flow Conditions
Minute Volume (L/min)
OC Flow (L/min) 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 13
0.5 23.5 23.5 22.8 23.0 23.0 21.3 21.0 21.0
1 32.7 30.3 28.3 28.0 27.3 24.0 24.0 23.0
2 43.3 37.7 35.0 33.0 32.5 31.8 31.0 30.0
3 53.5 44.8 41.0 38.8 37.3 36.0 35.3 33.5
4 63.5 53.5 47.3 44.5 42.5 40.5 39.8 37.8
5 72.8 61.3 53.8 49.8 48.0 45.5 44.0 41.0
6 79.3 68.3 59.5 55.5 53.0 50.0 48.0 44.3
7 84.5 74.0 65.0 60.0 57.3 54.3 52.3 48.0
8 87.3 79.0 70.0 66.5 62.0 58.0 56.0 51.0
9 89.0 82.8 75.0 71.0 66.3 60.8 58.5 53.0
10 88.5 84.3 79.3 75.5 69.0 65.5 62.3 56.8
Fio = fraction of inspired oxygen; OC = oxygen concentrator.
2
32 Journal of Special Operations Medicine Volume 15, Edition 3/Fall 2016