Page 77 - Journal of Special Operations Medicine - Spring 2015
P. 77
in persons who are obese, under the influence of stimu a long history of safety in patients with delirium. This class
lant drugs, and have underlying medical disease. The of drugs may increase the QTinterval of the cardiac cycle,
26
ideal medication for this purpose would be administered which can give rise to ventricular arrhythmias, including
intramuscularly (IM) or intranasally (IN), have a rapid ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia. In
onset of action, be of short duration, be effective on most rare cases, antipsychotic medications can trigger the neu
agitated or violent persons, and be free of hemodynamic roleptic malignant syndrome (NMS), resulting in hyper
instability and respiratory depression. While a medication thermia. The benefits of using antipsychotic medications
meeting all these criteria does not exist, sedation can be such as haloperidol in patients with ExDS generally out
accomplished by administering benzodiazepines, antipsy weigh the low risk of medication side effects, particularly
chotics, or a dissociative agent such as ketamine (Table 3). when limited to a single dose for initial control.
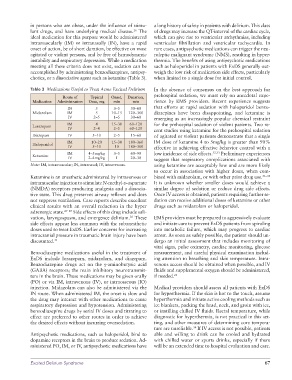
Table 3 Medications Useful to Treat Acute Excited Delirium In the absence of consensus on the best approach for
Route of Typical Onset, Duration, prehospital sedation, we must rely on anecdotal expe
Medication Administration Dose, mg min min rience by EMS providers. Recent experience suggests
IN 5 3–5 30–60 that efforts at rapid sedation with haloperidol benzo
Midazolam IM 5 10–15 120–360 diazepines have been disappointing, and ketamine is
IV 2–5 1–5 30–60 emerging as an increasingly popular chemical restraint
IM 4 15–30 60–120 for the prehospital sedation of violent patients. Two re
Lorazepam
IV 2–4 2–5 60–120 cent studies using ketamine for the prehospital sedation
Diazepam IV 5–10 2–5 15–60 of agitated or violent patients demonstrate that a single
IM 10–20 15–30 180–360 IM dose of ketamine 4 to 5mg/kg is greater than 90%
Haloperidol
IV 5–10 10 180–360 effective in achieving effective behavior control with a
IM 4–5mg/kg 3–5 60–90 low incidence of side effects. 32,33 Preliminary experiences
Ketamine
IV 2–4mg/kg 1 20–30 suggest that respiratory complications associated with
Note: IM, intramuscular; IN, intranasal; IV, intravenous. using ketamine are acceptably low and are more likely
to occur in association with higher doses, when com
Ketamine is an anesthetic administered by intravenous or bined with midazolam, or with other prior drug use. 31–33
intramuscular injection to stimulate Nmethyldaspartate It is unknown whether smaller doses would achieve a
(NMDA) receptors producing analgesia and a dissocia similar degree of sedation or reduce drug side effects.
tive state. This drug preserves airway reflexes and does Once IV access is obtained, patients requiring further se
not suppress ventilation. Case reports describe excellent dation can receive additional doses of ketamine or other
clinical results with an overall reduction in the hyper drugs such as midazolam or haloperidol.
adrenergic state. 27–29 Side effects of this drug include sali
vation, laryngospasm, and emergence delirium. These EMS providers must be prepared to aggressively evaluate
30
side effects appear less common with the subanesthetic and initiate care to prevent ExDS patients from spiraling
doses used to treat ExDS. Earlier concerns for increasing into metabolic failure, which may progress to cardiac
intracranial pressure in traumatic brain injury have been arrest. As soon as safely possible, the patient should un
discounted. 31 dergo an initial assessment that includes monitoring of
vital signs, pulse oximetry, cardiac monitoring, glucose
Benzodiazepine medications useful in the treatment of measurement, and careful physical examination includ
ExDS include lorazepam, midazolam, and diazepam. ing attention to breathing and skin temperature. Intra
Benzodiazepine drugs act on the γaminobutyric acid venous access should be obtained when possible, and IV
(GABA) receptors; the main inhibitory neurotransmit fluids and supplemental oxygen should be administered,
ters in the brain. These medications may be given orally if needed. 23
(PO) or via IM, intravenous (IV), or intraosseous (IO)
injection. Midazolam can also be administered via the Medical providers should assess all patients with ExDS
IN route. When administered IM, the onset is slow and for hyperthermia. If the skin is hot to the touch, assume
the drug may interact with other medications to cause hyperthermia and initiate active cooling methods such as
respiratory depression and hypotension. Administering ice blankets, packing the head, neck, and groin with ice,
benzodiazepine drugs by serial IV doses and titrating to or instilling chilled IV fluids. Rectal temperature, while
effect are preferred to other routes in order to achieve diagnostic for hyperthermia, is not practical in this set
the desired effects without incurring oversedation. ting, and other measures of determining core tempera
ture are unreliable. If IV access is not possible, patients
34
Antipsychotic medications, such as haloperidol, bind to able and willing to drink can be cooled and hydrated
dopamine receptors in the brain to produce sedation. Ad with chilled water or sports drinks, especially if there
ministered PO, IM, or IV, antipsychotic medications have will be an extended time to hospital evaluation and care.
Excited Delirium Syndrome 67